Immunomodulatory Activity of Polysaccharides Isolated from Saussurea salicifolia L. and Saussurea frolovii Ledeb
- PMID: 37764432
- PMCID: PMC10536955
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28186655
Immunomodulatory Activity of Polysaccharides Isolated from Saussurea salicifolia L. and Saussurea frolovii Ledeb
Abstract
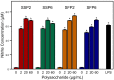
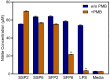
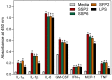
The genus Saussurea has been used in the preparation of therapies for a number of medical problems, yet not much is known about the therapeutic high-molecular-weight compounds present in extracts from these plants. Since polysaccharides are important in immune modulation, we investigated the chemical composition and immunomodulatory activity of Saussurea salicifolia L. and Saussurea frolovii Ledeb polysaccharides. Water-soluble polysaccharides from the aerial parts of these plants were extracted using water at pHs of 2 and 6 and subsequently precipitated in ethanol to obtain fractions SSP2 and SSP6 from S. salicifolia and fractions SSF2 and SSF6 from S. frolovii. The molecular weights of fractions SSP2, SSP6, SFP2, and SFP6 were estimated to be 143.7, 113.2, 75.3, and 64.3 kDa, respectively. The polysaccharides from S. frolovii contained xylose (67.1-71.7%) and glucose (28.3-32.9%), whereas the polysaccharides from S. frolovii contained xylose (63.1-76.7%), glucose (11.8-19.2%), galactose (4.7-8.3%), and rhamnose (6.8-9.4%). Fractions SSP2, SSP6, and SFP2 stimulated nitric oxide (NO) production by murine macrophages, and NO production induced by SSP2, SSP6, and SFP2 was not inhibited by polymyxin B treatment of the fractions, whereaspolymyxin B treatment diminished the effects of SFP6, suggesting that SFP6 could contain lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The LPS-free fractions SSP2, SSP6, and SFP2 had potent immunomodulatory activity, induced NO production, and activated transcription factors NF-κB/AP-1 in human monocytic THP-1 cells and cytokine production by human MonoMac-6 monocytic cells, including interleukin (IL)-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), interferon-γ, monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF). These data suggest that at least part of the beneficial therapeutic effects reported for water extracts of the Saussurea species are due to the modulation of leukocyte functions by polysaccharides.
Keywords: Saussurea; cytokine; macrophage; nitric oxide; plant polysaccharide; polymyxin B; xyloglucan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharides isolated from Alchornea cordifolia.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Mar 7;146(1):232-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.12.037. Epub 2013 Jan 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23291534 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharides isolated from Clerodendrum splendens: beneficial effects in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013 Jun 28;13:149. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-149. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013. PMID: 23806004 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Polysaccharides Isolated from Saussurea salicifolia (L.) DC on Th2-Dependent Immune Response.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2024 Aug;177(4):470-475. doi: 10.1007/s10517-024-06210-z. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39264566
-
Immunomodulatory and hemagglutinating activities of acidic polysaccharides isolated from Combretum racemosum.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Mar;15(3):628-37. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.01.015. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23380150 Free PMC article.
-
Morchella esculenta polysaccharides: a functional food with potential immunomodulatory properties.Nat Prod Res. 2025 May 27:1-12. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2025.2511160. Online ahead of print. Nat Prod Res. 2025. PMID: 40425301 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural Characterization and Immunoenhancing Properties of Polysaccharide CPTM-P1 from Taxus media.Molecules. 2024 Mar 19;29(6):1370. doi: 10.3390/molecules29061370. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38543007 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of the process of acetylation and carboxymethylation for a polysaccharide from Gastrodia elata and antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities test.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 12;15(1):8460. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93190-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40069382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chik W.I., Zhu L., Fan L.L., Yi T., Zhu G.Y., Gou X.J., Tang Y.N., Xu J., Yeung W.P., Zhao Z.Z., et al. Saussurea involucrata: A review of the botany, phytochemistry and ethnopharmacology of a rare traditional herbal medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015;172:44–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.06.033. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maqsood S., Miana G.A., Kanwal M., Malik S., Saleem S., Maqsood A., Rehman H., Hayat S., Farooq M.U. Phytochemical investigation and pharmacological evaluation of methanolic flower extract of Saussurea heteromalla. Pakistan J. Pharmaceut. Sci. 2022;35:1153–1158. - PubMed
-
- Naseer S., Iqbal J., Naseer A., Kanwal S., Hussain I., Tan Y., Aguilar-Marcelino L., Cossio-Bayugar R., Zajac Z., Bin Jardan Y.A., et al. Deciphering chemical profiling, pharmacological responses and potential bioactive constituents of Saussurea lappa Decne. Extracts through in vitro approaches. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022;29:1355–1366. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.01.040. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

