Advances in 4-Hydroxyphenylacetate-3-hydroxylase Monooxygenase
- PMID: 37764475
- PMCID: PMC10537072
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28186699
Advances in 4-Hydroxyphenylacetate-3-hydroxylase Monooxygenase
Abstract
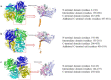
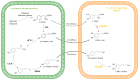
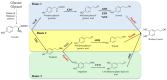
Catechols have important applications in the pharmaceutical, food, cosmetic, and functional material industries. 4-hydroxyphenylacetate-3-hydroxylase (4HPA3H), a two-component enzyme system comprising HpaB (monooxygenase) and HpaC (FAD oxidoreductase), demonstrates significant potential for catechol production because it can be easily expressed, is highly active, and exhibits ortho-hydroxylation activity toward a broad spectrum of phenol substrates. HpaB determines the ortho-hydroxylation efficiency and substrate spectrum of the enzyme; therefore, studying its structure-activity relationship, improving its properties, and developing a robust HpaB-conducting system are of significance and value; indeed, considerable efforts have been made in these areas in recent decades. Here, we review the classification, molecular structure, catalytic mechanism, primary efforts in protein engineering, and industrial applications of HpaB in catechol synthesis. Current trends in the further investigation of HpaB are also discussed.
Keywords: 4-hydroxyphenylacetate-3-hydroxylase monooxygenase; biocatalysis; catechols; protein engineering; structural property.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Characterization of 4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase (HpaB) of Escherichia coli as a reduced flavin adenine dinucleotide-utilizing monooxygenase.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000 Feb;66(2):481-6. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.2.481-486.2000. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10653707 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of enzymatic properties of two novel enzymes, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate dioxygenase and 4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase, from Sulfobacillus acidophilus TPY.BMC Microbiol. 2019 Feb 13;19(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1415-9. BMC Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30760216 Free PMC article.
-
4-Hydroxyphenylacetate 3-Hydroxylase (4HPA3H): A Vigorous Monooxygenase for Versatile O-Hydroxylation Applications in the Biosynthesis of Phenolic Derivatives.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 19;25(2):1222. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021222. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coordinated production and utilization of FADH2 by NAD(P)H-flavin oxidoreductase and 4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-monooxygenase.Biochemistry. 2003 Jun 24;42(24):7509-17. doi: 10.1021/bi034092r. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12809507
-
Monooxygenation of aromatic compounds by flavin-dependent monooxygenases.Protein Sci. 2019 Jan;28(1):8-29. doi: 10.1002/pro.3525. Protein Sci. 2019. PMID: 30311986 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hu S., Tang Y., Liu L. Adsorption Kinetics of Tea Waste to Catechins. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Agric. Life Sci.) 2014;40:679–687.
-
- Li Z., Li P., Deng C., Luo H. Piceatannol Inhibits Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion. Chin. J. Pathophysiol. 2017;12:1130–1133.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

