Comparison of the Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Propolis from Urban Apiaries
- PMID: 37764522
- PMCID: PMC10537721
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28186744
Comparison of the Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Propolis from Urban Apiaries
Abstract
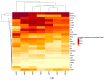
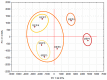
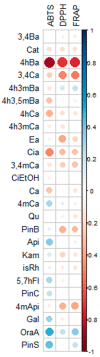
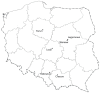
Bee products from urban apiaries are increasingly used. They are mainly used to promote local apiaries and cities in which they are located. The aim of the study was to compare the chemical composition and antioxidant activity of propolis from 6 Polish apiaries located in cities (Legionowo, Torun, Cracow, Warsaw, Katowice, Lodz). The chemical composition was analyzed using liquid chromatography (HPLC-DAD) and the analysis of antioxidant activity by scavenging free radicals (ABTS and DPPH) and FRAP. The obtained results showed the presence of 24 phenolic compounds in propolis extracts. The tested samples showed differentiation in terms of the content of individual chemical components, however, cinnamic acid and its derivatives were dominant. High antioxidant activity of the tested extracts was demonstrated (ABTS was in the range of 16.80-51.53 mg Te/mL, DPPH was in the range of 7.54-22.13 mg Te/mL, while FRAP reduction was in the range of 10.93-29.55 mg Te/mL). The obtained results compared with literature data on propolis from agricultural areas allow to conclude that propolis samples from both Poland types of areas are similar and can be classified as poplar propolis.
Keywords: antioxidants; chemical composition; propolis; urban apiares.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Machado C.S., Mokochinski J.B., de Lira T.O., Oliveira F.d.C.E.d., Cardoso M.V., Ferreira R.G., Sawaya A.C.H.F., Ferreira A.G., Pessoa C., Cuesta-Rubio O., et al. Comparative Study of Chemical Composition and Biological Activity of Yellow, Green, Brown, and Red Brazilian Propolis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016;2016:6057650. doi: 10.1155/2016/6057650. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

