Rapid SERS Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A
- PMID: 37764560
- PMCID: PMC10535226
- DOI: 10.3390/nano13182531
Rapid SERS Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A
Abstract
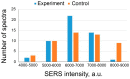
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) is a powerful technique for decoding of 2-5-component mixes of analytes. Low concentrations of analytes and complex biological media are usually non-decodable with SERS. Recognition molecules, such as antibodies and aptamers, provide an opportunity for a specific binding of ultra-low contents of analyte dissolved in complex biological media. Different approaches have been proposed to provide changes in SERS intensity of an external label upon binding of ultra-low contents of the analytes. In this paper, we propose a SERS-based sensor for the rapid and sensitive detection of botulinum toxin type A. The silver nanoisland SERS substrate was functionalized using an aptamer conjugated with a Raman label. The binding of the target affects the orientation of the label, providing changes in an analytical signal. This trick allowed detecting botulinum toxin type A in a one-stage manner without additional staining with a monotonous dose dependence and a limit of detection of 2.4 ng/mL. The proposed sensor architecture is consistent with the multiarray detection systems for multiplex analyses.
Keywords: SERS; aptamer; aptasensor; biosensor; botulinum neurotoxin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

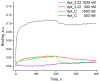

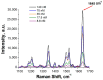




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

