Stand Up to Stand Out: Natural Dietary Polyphenols Curcumin, Resveratrol, and Gossypol as Potential Therapeutic Candidates against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection
- PMID: 37764669
- PMCID: PMC10535599
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15183885
Stand Up to Stand Out: Natural Dietary Polyphenols Curcumin, Resveratrol, and Gossypol as Potential Therapeutic Candidates against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection
Abstract
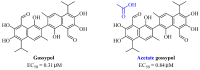
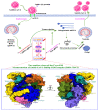
The COVID-19 pandemic has stimulated collaborative drug discovery efforts in academia and the industry with the aim of developing therapies and vaccines that target SARS-CoV-2. Several novel therapies have been approved and deployed in the last three years. However, their clinical application has revealed limitations due to the rapid emergence of viral variants. Therefore, the development of next-generation SARS-CoV-2 therapeutic agents with a high potency and safety profile remains a high priority for global health. Increasing awareness of the "back to nature" approach for improving human health has prompted renewed interest in natural products, especially dietary polyphenols, as an additional therapeutic strategy to treat SARS-CoV-2 patients, owing to its good safety profile, exceptional nutritional value, health-promoting benefits (including potential antiviral properties), affordability, and availability. Herein, we describe the biological properties and pleiotropic molecular mechanisms of dietary polyphenols curcumin, resveratrol, and gossypol as inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants as observed in in vitro and in vivo studies. Based on the advantages and disadvantages of dietary polyphenols and to obtain maximal benefits, several strategies such as nanotechnology (e.g., curcumin-incorporated nanofibrous membranes with antibacterial-antiviral ability), lead optimization (e.g., a methylated analog of curcumin), combination therapies (e.g., a specific combination of plant extracts and micronutrients), and broad-spectrum activities (e.g., gossypol broadly inhibits coronaviruses) have also been emphasized as positive factors in the facilitation of anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug development to support effective long-term pandemic management and control.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; broad-spectrum activities; combination therapies; curcumin; gossypol; lead optimization; nanotechnology; natural dietary polyphenols; resveratrol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationship that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Therapeutic Potential of Natural Dietary Flavonoids against SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 3;15(15):3443. doi: 10.3390/nu15153443. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37571380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gossypol Broadly Inhibits Coronaviruses by Targeting RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerases.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Dec;9(35):e2203499. doi: 10.1002/advs.202203499. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 36266926 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of polyphenols against complications of COVID-19: current evidence and potential efficacy.Pharmacol Rep. 2024 Apr;76(2):307-327. doi: 10.1007/s43440-024-00585-6. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Pharmacol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38498260 Review.
-
Plant-derived natural polyphenols as potential antiviral drugs against SARS-CoV-2 via RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) inhibition: an in-silico analysis.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021 Oct;39(16):6249-6264. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1796810. Epub 2020 Jul 28. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021. PMID: 32720577 Free PMC article.
-
Effective inhibition of coronavirus replication by Polygonum cuspidatum.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2021 Oct 30;26(10):789-798. doi: 10.52586/4988. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2021. PMID: 34719206
Cited by
-
Game Changers: Blockbuster Small-Molecule Drugs Approved by the FDA in 2024.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 15;18(5):729. doi: 10.3390/ph18050729. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Antiviral Activity of Polyphenols.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2025 Aug;69(15):e70042. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.70042. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2025. PMID: 40166854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A hypovirulence-associated capsidless bi-segmented ssRNA mycovirus enhances melanin and microsclerotial production in a vascular phytopathogenic fungus.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Aug 11;21(8):e1013348. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013348. eCollection 2025 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40788970 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxytyrosol Counteracts Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cell Dissemination via Its Copper Complexing Properties.Biology (Basel). 2023 Nov 16;12(11):1437. doi: 10.3390/biology12111437. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998036 Free PMC article.
-
Current View on Major Natural Compounds Endowed with Antibacterial and Antiviral Effects.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jun 28;13(7):603. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070603. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061285 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

