Unraveling the Gut Microbiome-Diet Connection: Exploring the Impact of Digital Precision and Personalized Nutrition on Microbiota Composition and Host Physiology
- PMID: 37764715
- PMCID: PMC10537332
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15183931
Unraveling the Gut Microbiome-Diet Connection: Exploring the Impact of Digital Precision and Personalized Nutrition on Microbiota Composition and Host Physiology
Abstract
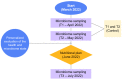
The human gut microbiome, an intricate ecosystem housing trillions of microorganisms within the gastrointestinal tract, holds significant importance in human health and the development of diseases. Recent advances in technology have allowed for an in-depth exploration of the gut microbiome, shedding light on its composition and functions. Of particular interest is the role of diet in shaping the gut microbiome, influencing its diversity, population size, and metabolic functions. Precision nutrition, a personalized approach based on individual characteristics, has shown promise in directly impacting the composition of the gut microbiome. However, to fully understand the long-term effects of specific diets and food components on the gut microbiome and to identify the variations between individuals, longitudinal studies are crucial. Additionally, precise methods for collecting dietary data, alongside the application of machine learning techniques, hold immense potential in comprehending the gut microbiome's response to diet and providing tailored lifestyle recommendations. In this study, we investigated the complex mechanisms that govern the diverse impacts of nutrients and specific foods on the equilibrium and functioning of the individual gut microbiome of seven volunteers (four females and three males) with an average age of 40.9 ± 10.3 years, aiming at identifying potential therapeutic targets, thus making valuable contributions to the field of personalized nutrition. These findings have the potential to revolutionize the development of highly effective strategies that are tailored to individual requirements for the management and treatment of various diseases.
Keywords: dietary intervention; gut microbiome; longitudinal studies; nutrigenomics; personalized medicine; precision nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

