Molecular Epidemiology and Genetic Diversity of Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Sicily during Pre- and Post-COVID-19 Surveillance Seasons
- PMID: 37764907
- PMCID: PMC10534943
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12091099
Molecular Epidemiology and Genetic Diversity of Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Sicily during Pre- and Post-COVID-19 Surveillance Seasons
Abstract
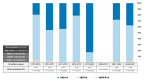
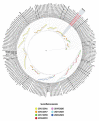
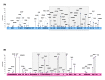
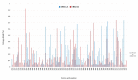
Human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) is an important pathogen of acute respiratory tract infection of global significance. In this study, we investigated the molecular epidemiology and the genetic variability of hRSV over seven surveillance seasons between 2015 and 2023 in Sicily, Italy. hRSV subgroups co-circulated through every season, although hRSV-B mostly prevailed. After the considerable reduction in the circulation of hRSV due to the widespread implementation of non-pharmaceutical preventive measures during the COVID-19 pandemic, hRSV rapidly re-emerged at a high intensity in 2022-2023. The G gene was sequenced for genotyping and analysis of deduced amino acids. A total of 128 hRSV-A and 179 hRSV-B G gene sequences were obtained. The phylogenetic analysis revealed that the GA2.3.5a (ON1) and GB5.0.5a (BA9) genotypes were responsible for the hRSV epidemics in Sicily.; only one strain belonged to the genotype GB5.0.4a. No differences were observed in the circulating genotypes during pre- and post-pandemic years. Amino acid sequence alignment revealed the continuous evolution of the G gene, with a combination of amino acid changes specifically appearing in 2022-2023. The predicted N-glycosylation sites were relatively conserved in ON1 and BA9 genotype strains. Our findings augment the understanding and prediction of the seasonal evolution of hRSV at the local level and its implication in the monitoring of novel variants worth considering in better design of candidate vaccines.
Keywords: BA9; GA2.3.5a; GB5.0.4a; GB5.0.5a; Italy; ON1; Sicily; genotype; hRSV-A; hRSV-B; molecular epidemiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Li Y., Wang X., Blau D.M., Caballero M.T., Feikin D.R., Gill C.J., Madhi S.A., Omer S.B., Simões E.A.F., Campbell H., et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in children younger than 5 years in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet. 2022;399:2047–2064. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00478-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Savic M., Penders Y., Shi T., Branche A., Pirçon J.Y. Respiratory syncytial virus disease burden in adults aged 60 years and older in high-income countries: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses. 2023;17:e13031. doi: 10.1111/irv.13031. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shi T., Vennard S., Jasiewicz F., Brogden R., Nair H., RESCEU Investigators Disease Burden Estimates of Respiratory Syncytial Virus related Acute Respiratory Infections in Adults With Comorbidity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Infect. Dis. 2022;226:S17–S21. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiab040. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pierangeli A., Nenna R., Fracella M., Scagnolari C., Oliveto G., Sorrentino L., Frasca F., Conti M.G., Petrarca L., Papoff P., et al. Genetic diversity and its impact on disease severity in respiratory syncytial virus subtype-A and -B bronchiolitis before and after pandemic restrictions in Rome. J. Infect. 2023:S0163-4453(23)00381-X. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2023.07.008. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

