Monocytes from Uninfected Neonates Born to Trypanosoma cruzi-Infected Mothers Display Upregulated Capacity to Produce TNF-α and to Control Infection in Association with Maternally Transferred Antibodies
- PMID: 37764911
- PMCID: PMC10536721
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12091103
Monocytes from Uninfected Neonates Born to Trypanosoma cruzi-Infected Mothers Display Upregulated Capacity to Produce TNF-α and to Control Infection in Association with Maternally Transferred Antibodies
Abstract
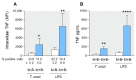
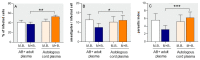
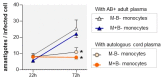
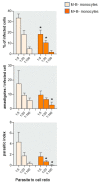
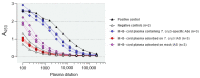
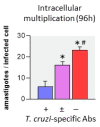
Activated monocytes/macrophages that produce inflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide are crucial for controlling Trypanosoma cruzi infection. We previously showed that uninfected newborns from T. cruzi infected mothers (M+B- newborns) were sensitized to produce higher levels of inflammatory cytokines than newborns from uninfected mothers (M-B- newborns), suggesting that their monocytes were more activated. Thus, we wondered whether these cells might help limit congenital infection. We investigated this possibility by studying the activation status of M+B- cord blood monocytes and their ability to control T. cruzi in vitro infection. We showed that M+B- monocytes have an upregulated capacity to produce the inflammatory cytokine TNF-α and a better ability to control T. cruzi infection than M-B- monocytes. Our study also showed that T. cruzi-specific Abs transferred from the mother play a dual role by favoring trypomastigote entry into M+B- monocytes and inhibiting intracellular amastigote multiplication. These results support the possibility that some M+B- fetuses may eliminate the parasite transmitted in utero from their mothers, thus being uninfected at birth.
Keywords: Trypanosoma cruzi-specific antibodies; congenital chagas disease; monocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Immune responses of non-infected neonates of mothers infected with Trypanosoma cruzi].Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2005;38 Suppl 2:96-100. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2005. PMID: 16482825 Spanish.
-
Maternal Trypanosoma cruzi infection upregulates capacity of uninfected neonate cells To produce pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines.Infect Immun. 2000 Sep;68(9):5430-4. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.9.5430-5434.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10948177 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal infection with Trypanosoma cruzi and congenital Chagas disease induce a trend to a type 1 polarization of infant immune responses to vaccines.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009 Dec 22;3(12):e571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000571. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009. PMID: 20041029 Free PMC article.
-
Trypanosoma cruzi Infection at the Maternal-Fetal Interface: Implications of Parasite Load in the Congenital Transmission and Challenges in the Diagnosis of Infected Newborns.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jun 7;10:1250. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01250. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31231337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Role of cytokines in resistance and pathology in Trypanosoma cruzi infection].Rev Argent Microbiol. 1996 Apr-Jun;28(2):99-109. Rev Argent Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8768488 Review. Spanish.
References
-
- Carlier Y., Altcheh J., Angheben A., Freilij H., Luquetti A.O., Schijman A.G., Segovia M., Wagner N., Albajar Vinas P. Congenital Chagas Disease: Updated Recommendations for Prevention, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Follow-up of Newborns and Siblings, Girls, Women of Childbearing Age, and Pregnant Women. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019;13:e0007694. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007694. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- Centre de Recherche Interuniversitaire en Vaccinologie" (CRIV)/Région Wallonne (Namur, Belgium) and Glaxo-Smithkline Biologicals (Rixensart, Belgium)
- Conseil Interuniversitaire de la Communauté française de Belgique (CIUF)
- Fonds Emile Defay and David and Fonds Alice Van Buuren/Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB)
- 3461505F and 9-452804/Fund for Scientific Research
- ELAC2014/HID-0328 and ERANet17/HLH-0142/ERANET-LAC
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

