One Health Spread of 16S Ribosomal RNA Methyltransferase-Harboring Gram-Negative Bacterial Genomes: An Overview of the Americas
- PMID: 37764972
- PMCID: PMC10536106
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12091164
One Health Spread of 16S Ribosomal RNA Methyltransferase-Harboring Gram-Negative Bacterial Genomes: An Overview of the Americas
Abstract
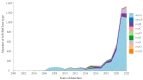
Aminoglycoside antimicrobials remain valuable therapeutic options, but their effectiveness has been threatened by the production of bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA methyltransferases (16S-RMTases). In this study, we evaluated the genomic epidemiology of 16S-RMTase genes among Gram-negative bacteria circulating in the American continent. A total of 4877 16S-RMTase sequences were identified mainly in Enterobacterales and nonfermenting Gram-negative bacilli isolated from humans, animals, foods, and the environment during 1931-2023. Most of the sequences identified were found in the United States, Brazil, Canada, and Mexico, and the prevalence of 16S-RMTase genes have increased in the last five years (2018-2022). The three species most frequently carrying 16S-RMTase genes were Acinetobacter baummannii, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Escherichia coli. The armA gene was the most prevalent, but other 16S-RMTase genes (e.g., rmtB, rmtE, and rmtF) could be emerging backstage. More than 90% of 16S-RMTase sequences in the Americas were found in North American countries, and although the 16S-RMTase genes were less prevalent in Central and South American countries, these findings may be underestimations due to limited genomic data. Therefore, whole-genome sequence-based studies focusing on aminoglycoside resistance using a One Health approach in low- and middle-income countries should be encouraged.
Keywords: 16S-RMTase; Acinetobacter baumannii; Enterobacterales; One Health; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; aminoglycoside resistance; armA; rmtB; rmtF.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A prospective surveillance study to determine the prevalence of 16S rRNA methyltransferase-producing Gram-negative bacteria in the UK.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021 Aug 12;76(9):2428-2436. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab186. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021. PMID: 34142130
-
Novel 16S rRNA methyltransferase RmtE3 in Acinetobacter baumannii ST79.J Med Microbiol. 2022 May;71(5). doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001531. J Med Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35588089
-
In vitro activity of apramycin against 16S-RMTase-producing Gram-negative isolates.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2023 Jun;33:21-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2023.02.005. Epub 2023 Feb 22. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2023. PMID: 36822368
-
Aminoglycoside Resistance: The Emergence of Acquired 16S Ribosomal RNA Methyltransferases.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2016 Jun;30(2):523-537. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2016.02.011. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2016. PMID: 27208771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exogenously acquired 16S rRNA methyltransferases found in aminoglycoside-resistant pathogenic Gram-negative bacteria: an update.Drug Resist Updat. 2012 Jun;15(3):133-48. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2012.05.001. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Drug Resist Updat. 2012. PMID: 22673098 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of First-in-Class Inhibitors Targeting a Pathogen-Associated Aminoglycoside-Resistance 16S rRNA Methyltransferase.ACS Infect Dis. 2025 Aug 8;11(8):2276-2286. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.5c00297. Epub 2025 Jul 11. ACS Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40643688 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of blaNDM-5 and blaOXA-232 Positive Colistin- and Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Bulgarian Hospital.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jul 21;13(7):677. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070677. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061359 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: genetic control mechanisms and therapeutic advances.Mol Biomed. 2024 Nov 27;5(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s43556-024-00221-y. Mol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 39592545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of in vitro susceptibility and resistance mechanisms to amikacin among diverse carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Oct 1;17(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-02016-0. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39354545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uddin T.M., Chakraborty A.J., Khusro A., Zidan B.R.M., Mitra S., Bin Emran T., Dhama K., Ripon K.H., Gajdács M., Sahibzada M.U.K., et al. Antibiotic resistance in microbes: History, mechanisms, therapeutic strategies and future prospects. J. Infect. Public Heal. 2021;14:1750–1766. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2021.10.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fuga B., Sellera F.P., Cerdeira L., Esposito F., Cardoso B., Fontana H., Moura Q., Cardenas-Arias A., Sano E., Ribas R.M., et al. WHO Critical Priority Escherichia coli as One Health Challenge for a Post-Pandemic Scenario: Genomic Surveillance and Analysis of Current Trends in Brazil. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022;10:e0125621. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01256-21. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

