Research Progress of Flavonoids Regulating Endothelial Function
- PMID: 37765009
- PMCID: PMC10534649
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16091201
Research Progress of Flavonoids Regulating Endothelial Function
Abstract
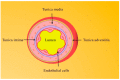
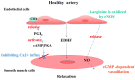
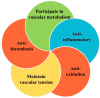
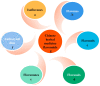
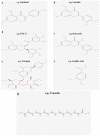
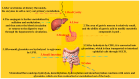
The endothelium, as the guardian of vascular homeostasis, is closely related to the occurrence and development of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). As an early marker of the development of a series of vascular diseases, endothelial dysfunction is often accompanied by oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Natural flavonoids in fruits, vegetables, and Chinese herbal medicines have been shown to induce and regulate endothelial cells and exert anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative stress, and anti-aging effects in a large number of in vitro models and in vivo experiments so as to achieve the prevention and improvement of cardiovascular disease. Focusing on endothelial mediation, this paper introduces the signaling pathways involved in the improvement of endothelial dysfunction by common dietary and flavonoids in traditional Chinese medicine and describes them based on their metabolism in the human body and their relationship with the intestinal flora. The aim of this paper is to demonstrate the broad pharmacological activity and target development potential of flavonoids as food supplements and drug components in regulating endothelial function and thus in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. This paper also introduces the application of some new nanoparticle carriers in order to improve their bioavailability in the human body and play a broader role in vascular protection.
Keywords: NO; bioavailability; endothelial dysfunction; flavonoids; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress.J Adv Res. 2021 Jul 6;34:43-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.06.023. eCollection 2021 Dec. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 35024180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural flavonoids derived from herbal medicines are potential anti-atherogenic agents by inhibiting oxidative stress in endothelial cells.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 24;14:1141180. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1141180. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36909175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors modulating bioavailability of quercetin-related flavonoids and the consequences of their vascular function.Biochem Pharmacol. 2017 Sep 1;139:15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.03.021. Epub 2017 Apr 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28377278 Review.
-
Advancement of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Regulation of Intestinal Flora: Mechanism-based Role in Disease Management.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2022;17(2):136-144. doi: 10.2174/1574892816666210929164930. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 34587887 Review.
-
Inhibition of Endothelial Dysfunction by Dietary Flavonoids and Preventive Effects Against Cardiovascular Disease.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020 Jan;75(1):1-9. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000757. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31613843 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting miRNA with flavonoids: unlocking novel pathways in cardiovascular disease management.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 6;16:1532986. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1532986. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40115258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the Chemical Composition and Biofunctionality of Hericium spp. Fungi: A Comprehensive Overview.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 29;25(11):5949. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115949. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inverse associations between dietary flavonoid and subclass intakes and frailty in U.S. adults.Front Nutr. 2025 May 16;12:1490998. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1490998. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40453721 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Flavonoid Research: Sources, Biological Activities, and Developmental Prospectives.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Mar 26;46(4):2884-2925. doi: 10.3390/cimb46040181. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38666911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Licorice Extract Isoliquiritigenin Protects Endothelial Function in Type 2 Diabetic Mice.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 19;16(18):3160. doi: 10.3390/nu16183160. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sacks F.M., Lichtenstein A.H., Wu J.H.Y., Appel L.J., Creager M.A., Kris-Etherton P.M., Miller M., Rimm E.B., Rudel L.L., Robinson J.G., et al. Dietary Fats and Cardiovascular Disease: A Presidential Advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;136:e1–e23. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000510. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

