Continuous Manufacturing of Solvent-Free Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Enhanced Drug Solubility via Hot-Melt Extrusion: A Quality by Design Approach
- PMID: 37765172
- PMCID: PMC10536280
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092203
Continuous Manufacturing of Solvent-Free Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Enhanced Drug Solubility via Hot-Melt Extrusion: A Quality by Design Approach
Abstract
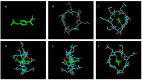
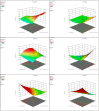
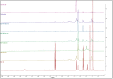
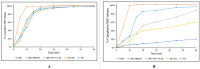
Conventional cyclodextrin complexation enhances the solubility of poorly soluble drugs but is solvent-intensive and environmentally unfavorable. This study evaluated solvent-free hot-melt extrusion (HME) for forming cyclodextrin inclusion complexes to improve the solubility and dissolution of ibuprofen (IBU). Molecular docking confirmed IBU's hosting in Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβ-CD), while phase solubility revealed its complex stoichiometry and stability. In addition, an 11 mm twin-screw co-rotating extruder with PVP VA-64 as an auxiliary substance aided the complex formation and extrusion. Using QbD and the Box-Behnken design, we studied variables (barrel temperature, screw speed, and polymer concentration) and their impact on solubility and dissolution. The high polymer concentration and high screw speeds positively affected the dependent variables. However, higher temperatures had a negative effect. The lowest barrel temperature set near the Tg of the polymer, when combined with high polymer concentrations, resulted in high torques in HME and halted the extrusion process. Therefore, the temperature and polymer concentration should be selected to provide sufficient melt viscosities to aid the complex formation and extrusion process. Studies such as DSC and XRD revealed the amorphous conversion of IBU, while the inclusion complex formation was demonstrated by ATR and NMR studies. The dissolution of ternary inclusion complexes (TIC) produced from HME was found to be ≥85% released within 30 min. This finding implied the high solubility of IBU, according to the US FDA 2018 guidance for highly soluble compounds containing immediate-release solid oral dosage forms. Overall, the studies revealed the effect of various process parameters on the formation of CD inclusion complexes via HME.
Keywords: complexation; cyclodextrin; hot-melt extrusion; quality by design (QbD); solubility enhancement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Hot-melt extrusion as a continuous manufacturing process to form ternary cyclodextrin inclusion complexes.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017 Jan 1;96:590-597. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2016.09.032. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 27687637
-
Study the influence of formulation process parameters on solubility and dissolution enhancement of efavirenz solid solutions prepared by hot-melt extrusion: a QbD methodology.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018 Dec;8(6):1644-1657. doi: 10.1007/s13346-018-0481-0. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29426975
-
A New Extrudable Form of Hypromellose: AFFINISOL™ HPMC HME.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016 Feb;17(1):106-19. doi: 10.1208/s12249-015-0395-9. Epub 2015 Sep 4. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016. PMID: 26335416 Free PMC article.
-
Hot Melt Extruded and Injection Moulded Dosage Forms: Recent Research and Patents.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2015;9(3):194-200. doi: 10.2174/1872211309666150512111143. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2015. PMID: 27165308 Review.
-
Quality-by-design in hot melt extrusion based amorphous solid dispersions: An industrial perspective on product development.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021 Mar 1;158:105655. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105655. Epub 2020 Nov 28. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 33253883 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Approaches for Inclusion Complexes of Ezetimibe with Cyclodextrins: Strategies for Solubility Enhancement and Interaction Analysis via Molecular Docking.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 16;26(4):1686. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041686. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004150 Free PMC article.
-
Three-Dimensional Printing of Personalized Carbamazepine Tablets Using Hydrophilic Polymers: An Investigation of Correlation Between Dissolution Kinetics and Printing Parameters.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Aug 1;17(15):2126. doi: 10.3390/polym17152126. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40808174 Free PMC article.
-
Hot-Melt Extrusion: from Theory to Application in Pharmaceutical Formulation-Where Are We Now?AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Feb 14;25(2):37. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02749-2. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38355916 Review.
-
Twin Screw Melt Granulation of Simvastatin: Drug Solubility and Dissolution Rate Enhancement Using Polymer Blends.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Dec 23;16(12):1630. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121630. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39771607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyd B.J., Bergström C.A.S., Vinarov Z., Kuentz M., Brouwers J., Augustijns P., Brandl M., Bernkop-Schnürch A., Shrestha N., Préat V., et al. Successful Oral Delivery of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs Both Depends on the Intraluminal Behavior of Drugs and of Appropriate Advanced Drug Delivery Systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019;137:104967. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2019.104967. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alzahrani A., Nyavanandi D., Mandati P., Youssef A.A.A., Narala S., Bandari S., Repka M. A Systematic and Robust Assessment of Hot-Melt Extrusion-Based Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Theoretical Prediction to Practical Implementation. Int. J. Pharm. 2022;624:121951. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121951. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

