Twin Screw Melt Granulation: A Single Step Approach for Developing Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System for Lipophilic Drugs
- PMID: 37765237
- PMCID: PMC10534719
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092267
Twin Screw Melt Granulation: A Single Step Approach for Developing Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System for Lipophilic Drugs
Abstract
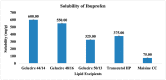
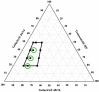
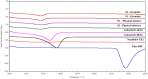
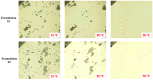
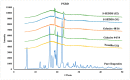
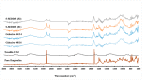
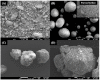
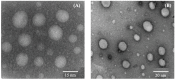
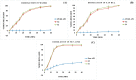
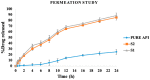
The current research aims to improve the solubility of the poorly soluble drug, i.e., ibuprofen, by developing self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) utilizing a twin screw melt granulation (TSMG) approach. Gelucire® 44/14, Gelucire® 48/16, and Transcutol® HP were screened as suitable excipients for developing the SEDDS formulations. Initially, liquid SEDDS (L-SEDDS) were developed with oil concentrations between 20-50% w/w and surfactant to co-surfactant ratios of 2:1, 4:1, 6:1. The stable formulations of L-SEDDS were transformed into solid SEDDS (S-SEDDS) using a suitable adsorbent carrier and compressed into tablets (T-SEDDS). The S-SEDDS has improved flow, drug release profiles, and permeability compared to pure drugs. The existence of the drug in an amorphous state was confirmed by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and powder X-ray diffraction analysis (PXRD). The formulations with 20% w/w and 30% w/w of oil concentration and a 4:1 ratio of surfactant to co-surfactant have resulted in a stable homogeneous emulsion with a globule size of 14.67 ± 0.23 nm and 18.54 ± 0.55 nm. The compressed tablets were found stable after six months of storage at accelerated and long-term conditions. This shows the suitability of the TSMG approach as a single-step continuous manufacturing process for developing S-SEDDS formulations.
Keywords: globule size; liquid SEDDS; polydispersity index; self-emulsifying drug delivery system; solid SEDDS; twin screw melt granulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kumar S., Dilbaghi N., Saharan R., Bhanjana G. Nanotechnology as Emerging Tool for Enhancing Solubility of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Bionanoscience. 2012;2:227–250. doi: 10.1007/s12668-012-0060-7. - DOI
-
- Sohail Arshad M., Zafar S., Yousef B., Alyassin Y., Ali R., AlAsiri A., Chang M.W., Ahmad Z., Ali Elkordy A., Faheem A., et al. A Review of Emerging Technologies Enabling Improved Solid Oral Dosage Form Manufacturing and Processing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021;178:113840. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.113840. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

