Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Improved Drug Bioavailability and Activity: Synthetic and Analytical Aspects
- PMID: 37765313
- PMCID: PMC10534465
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092345
Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Improved Drug Bioavailability and Activity: Synthetic and Analytical Aspects
Abstract
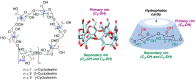
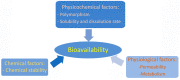
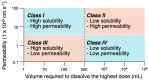
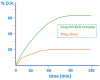
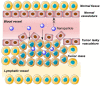
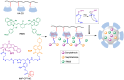
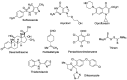
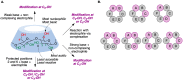
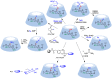
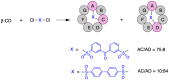
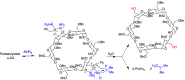
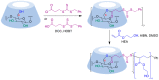
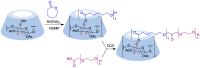
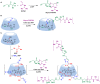
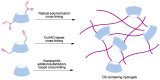
Many active pharmaceutical ingredients show low oral bioavailability due to factors such as poor solubility and physical and chemical instability. The formation of inclusion complexes with cyclodextrins, as well as cyclodextrin-based polymers, nanosponges, and nanofibers, is a valuable tool to improve the oral bioavailability of many drugs. The microencapsulation process modifies key properties of the included drugs including volatility, dissolution rate, bioavailability, and bioactivity. In this context, we present relevant examples of the stabilization of labile drugs through the encapsulation in cyclodextrins. The formation of inclusion complexes with drugs belonging to class IV in the biopharmaceutical classification system as an effective solution to increase their bioavailability is also discussed. The stabilization and improvement in nutraceuticals used as food supplements, which often have low intestinal absorption due to their poor solubility, is also considered. Cyclodextrin-based nanofibers, which are polymer-free and can be generated using environmentally friendly technologies, lead to dramatic bioavailability enhancements. The synthesis of chemically modified cyclodextrins, polymers, and nanosponges based on cyclodextrins is discussed. Analytical techniques that allow the characterization and verification of the formation of true inclusion complexes are also considered, taking into account the differences in the procedures for the formation of inclusion complexes in solution and in the solid state.
Keywords: anticancer drug carriers; bioavailability enhancement; cyclodextrin analytical techniques; cyclodextrin nanofibers; cyclodextrin synthesis; drug–cyclodextrin inclusion complexes; nanosponges.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
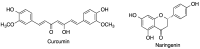
References
-
- Duchêne D., editor. New Trends in Cyclodextrins and Derivatives. Editions de Santé; Paris, France: 1991.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

