Fruit Quality and Metabolomic Analyses of Fresh Food Accessions Provide Insights into the Key Carbohydrate Metabolism in Blueberry
- PMID: 37765362
- PMCID: PMC10535370
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12183200
Fruit Quality and Metabolomic Analyses of Fresh Food Accessions Provide Insights into the Key Carbohydrate Metabolism in Blueberry
Abstract
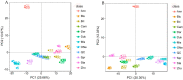
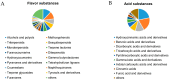
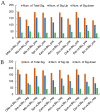
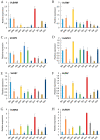
Blueberry is a nutrient-rich berry, and its taste and flavor directly determine the consumer preference. Until now, few studies have focused on the comparison of fresh food quality and the key metabolites in superior fresh-eating blueberry cultivars. Herein, fruit quality indicators of 10 highbush blueberry cultivars were evaluated using 'Bluerain' as the control. Appearance quality analysis of fruits showed that 'Brigitta' had a larger fruit size and 'Anna' was the smallest. 'Anna' fruits, followed by 'O'Neal', had the highest ratio of soluble solids to acidity because of their lowest titratable acidity content. Despite the high soluble sugar content, the antioxidants in 'Anna' fruits such as total flavonoids, anthocyanins and vitamin C were lowest among all cultivars, while 'Duke' seemed to have opposite patterns. Furthermore, a total of 553 and 557 metabolites were identified by non-targeted metabolomics liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) in positive and negative ion mode, respectively. Particularly, the numbers of differentially accumulated metabolites (DAMs) were the most between the 'O'Neal' vs. 'Bluerain' group. The DAMs involved in the metabolic pathways, sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid biosynthesis, monoterpenoid biosynthesis, galactose metabolism, starch and sucrose metabolism, may be mainly related to the synthesis of flavor and carbohydrate substances. Moreover, the expression patterns of genes involved in sugar metabolism were verified by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis in different cultivars. Therefore, the systematical comparison of the quality characteristics, metabolites and expression profiles of related genes in highbush blueberries with good flavor could provide some basis for further research on fresh fruit breeding of blueberries.
Keywords: LC-MS/MS; blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.); flavor profile; fresh food quality; sugar metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative anatomical and transcriptomic insights into Vaccinium corymbosum flower bud and fruit throughout development.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Jun 24;21(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03067-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34167466 Free PMC article.
-
Benzothiadiazole enhances ascorbate recycling and polyphenols accumulation in blueberry in a cultivar-dependent manner.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Dec 9;13:1032133. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1032133. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36570922 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Profiling Reveals the Variations in Carbohydrate Metabolism between Two Blueberry Cultivars.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 25;25(1):293. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010293. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203463 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and biochemical changes during fruit maturation and ripening in highbush blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.).Food Chem. 2023 Jun 1;410:135299. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135299. Epub 2022 Dec 24. Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 36608546
-
Full-length fruit transcriptomes of southern highbush (Vaccinium sp.) and rabbiteye (V. virgatum Ait.) blueberry.BMC Genomics. 2022 Oct 29;23(1):733. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08935-5. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36309640 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gosch C. Antioxidative effects of blueberries (Vaccinium sp.): An overview. Erwerbs Obstbau. 2003;45:117–124.
-
- Li D.N., Li B., Ma Y., Sun X.Y., Lin Y., Meng X.J. Polyphenols, anthocyanins, and flavonoids contents and the antioxidant capacity of various cultivars of highbush and half-high blueberries. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017;62:84–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2017.03.006. - DOI
-
- Kalt W., Ryan D.A.J., Duy J.C., Prior R.L., Ehlenfeldt M.K., Vander Kloet S.P. Interspecific variation in anthocyanins, phenolics, and antioxidant capacity among genotypes of highbush and lowbush blueberries (Vaccinium section cyanococcus spp.) J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001;49:4761–4767. doi: 10.1021/jf010653e. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Saftner R., Polashock J., Ehlenfeldt M., Vinyard B. Instrumental and sensory quality characteristics of blueberry fruit from twelve cultivars. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2008;49:19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2008.01.008. - DOI
-
- Gilbert J.L., Schwieterman M.L., Colquhoun T.A., Clark D.G., Olmstead J.W. Potential for increasing southern highbush blueberry flavor acceptance by breeding for major volatile components. HortScience. 2013;48:835–843. doi: 10.21273/hortsci.48.7.835. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

