Ultra-Wideband Radar for Simultaneous and Unobtrusive Monitoring of Respiratory and Heart Rates in Early Childhood: A Deep Transfer Learning Approach
- PMID: 37765721
- PMCID: PMC10535330
- DOI: 10.3390/s23187665
Ultra-Wideband Radar for Simultaneous and Unobtrusive Monitoring of Respiratory and Heart Rates in Early Childhood: A Deep Transfer Learning Approach
Abstract
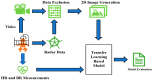
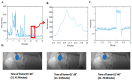
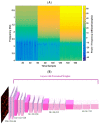
Unobtrusive monitoring of children's heart rate (HR) and respiratory rate (RR) can be valuable for promoting the early detection of potential health issues, improving communication with healthcare providers and reducing unnecessary hospital visits. A promising solution for wireless vital sign monitoring is radar technology. This paper presents a novel approach for the simultaneous estimation of children's RR and HR utilizing ultra-wideband (UWB) radar using a deep transfer learning algorithm in a cohort of 55 children. The HR and RR are calculated by processing radar signals via spectrogram from time epochs of 10 s (25 sample length of hamming window with 90% overlap) and then transforming the resultant representation into 2-dimensional images. These images were fed into a pre-trained Visual Geometry Group-16 (VGG-16) model (trained on ImageNet dataset), with weights of five added layers fine-tuned using the proposed data. The prediction on the test data achieved a mean absolute error (MAE) of 7.3 beats per minute (BPM < 6.5% of average HR) and 2.63 breaths per minute (BPM < 7% of average RR). We also achieved a significant Pearson's correlation of 77% and 81% between true and extracted for HR and RR, respectively. HR and RR samples are extracted every 10 s.
Keywords: UWB radar; early childhood; heart rate; monitor; respiratory rate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Serra A., Cocuzza S., Maiolino L., Abramo A., Spinato G., Tonoli G., Amadori M., Politi D., Tirelli G., Spinato R. The watch-pat in pediatrics sleep disordered breathing: Pilot study on children with negative nocturnal pulse oximetry. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017;97:245–250. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2017.04.021. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

