Intelligent ADL Recognition via IoT-Based Multimodal Deep Learning Framework
- PMID: 37765984
- PMCID: PMC10537500
- DOI: 10.3390/s23187927
Intelligent ADL Recognition via IoT-Based Multimodal Deep Learning Framework
Abstract
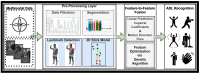
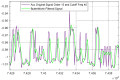
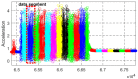
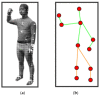
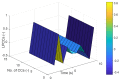
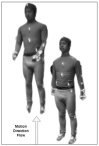
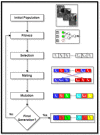
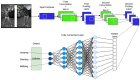
Smart home monitoring systems via internet of things (IoT) are required for taking care of elders at home. They provide the flexibility of monitoring elders remotely for their families and caregivers. Activities of daily living are an efficient way to effectively monitor elderly people at home and patients at caregiving facilities. The monitoring of such actions depends largely on IoT-based devices, either wireless or installed at different places. This paper proposes an effective and robust layered architecture using multisensory devices to recognize the activities of daily living from anywhere. Multimodality refers to the sensory devices of multiple types working together to achieve the objective of remote monitoring. Therefore, the proposed multimodal-based approach includes IoT devices, such as wearable inertial sensors and videos recorded during daily routines, fused together. The data from these multi-sensors have to be processed through a pre-processing layer through different stages, such as data filtration, segmentation, landmark detection, and 2D stick model. In next layer called the features processing, we have extracted, fused, and optimized different features from multimodal sensors. The final layer, called classification, has been utilized to recognize the activities of daily living via a deep learning technique known as convolutional neural network. It is observed from the proposed IoT-based multimodal layered system's results that an acceptable mean accuracy rate of 84.14% has been achieved.
Keywords: IoT; activities of daily living recognition; deep learning; multimodal data; patient monitoring; smart homes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ali M., Ali A.A., Taha A.-E., Dhaou I.B., Gia T.N. Intelligent Autonomous Elderly Patient Home Monitoring System; Proceedings of the ICC 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC); Shanghai, China. 21–23 May 2019; pp. 1–6. - DOI
-
- Madiha J., Ahmad J., Kim K. Wearable Sensors based Exertion Recognition using Statistical Features and Random Forest for Physical Healthcare Monitoring; Proceedings of the 2021 International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technologies (IBCAST); Islamabad, Pakistan. 12–16 January 2021; pp. 512–517. - DOI
-
- Zhou X., Zhang L. SA-FPN: An effective feature pyramid network for crowded human detection. Appl. Intell. 2022;52:12556–12568. doi: 10.1007/s10489-021-03121-8. - DOI
-
- Gaddam A., Mukhopadhyay S.C., Gupta G.S. Trial & experimentation of a smart home monitoring system for elderly; Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference; Hangzhou, China. 9–12 May 2011; pp. 1–6. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

