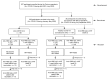
Immune Response after SARS-CoV-2 Infection with Residual Post-COVID Symptoms
- PMID: 37766091
- PMCID: PMC10535557
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11091413
Immune Response after SARS-CoV-2 Infection with Residual Post-COVID Symptoms
Abstract
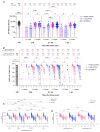
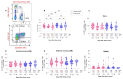
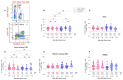
Many patients develop post-acute COVID syndrome (long COVID (LC)). We compared the immune response of LC and individuals with post-COVID full recovery (HC) during the Omicron pandemic. Two hundred ninety-two patients with confirmed COVID infections from January to May 2022 were enrolled. We observed anti-SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain immunoglobulin G, surrogate virus neutralization test, T cell subsets, and neutralizing antibodies against Wuhan, BA.1, and BA.5 viruses (NeuT). NeuT was markedly reduced against BA.1 and BA.5 in HC and LC groups, while antibodies were more sustained with three doses and an updated booster shot than ≤2-dose vaccinations. The viral neutralization ability declined at >84-days after COVID-19 onset (PC) in both groups. PD1-expressed central and effector memory CD4+ T cells, and central memory CD8+ T cells were reduced in the first months PC in LC. Therefore, booster vaccines may be required sooner after the most recent infection to rescue T cell function for people with symptomatic LC.
Keywords: Omicron; breakthrough infection; immunogenicity; long COVID; neutralizing antibody.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Tuekprakhon A., Nutalai R., Dijokaite-Guraliuc A., Zhou D., Ginn H.M., Selvaraj M., Liu C., Mentzer A.J., Supasa P., Duyvesteyn H.M.E., et al. Antibody escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 from vaccine and BA.1 serum. Cell. 2022;185:2422–2433.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scarpa F., Sanna D., Benvenuto D., Borsetti A., Azzena I., Casu M., Fiori P.L., Giovanetti M., Maruotti A., Ceccarelli G., et al. Genetic and structural data on the SARS-CoV-2 omicron BQ.1 variant reveal its low potential for epidemiological expansion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23:15264. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315264. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Thailand COVID-19—WHO Thailand Situation Reports. [(accessed on 30 April 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/thailand/emergencies/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio....
-
- UK Health Security Agency . SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern and Variants under Investigation in England: Technical Briefing 49. UK Health Security Agency; London, UK: 2023.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

