Exploring the Effects of Vitamin D and Vitamin A Levels on the Response to COVID-19 Vaccine
- PMID: 37766185
- PMCID: PMC10535137
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11091509
Exploring the Effects of Vitamin D and Vitamin A Levels on the Response to COVID-19 Vaccine
Abstract
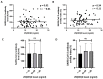
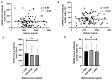
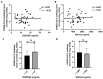
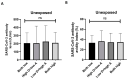
COVID-19 vaccines were developed at an unprecedented speed in history. The factors affecting the response to COVID-19 vaccines are not clear. Herein, the effects of vitamin D and vitamin A (retinol) levels on the response to the BNT162b2 vaccine were explored. A total of 124 vaccine recipients were recruited from the general population attending vaccination centers in Irbid, Jordan. Blood samples were collected immediately before receiving the first vaccine dose (D0) and three weeks later (D21). Baseline (D0) levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D], retinol, and SARS-CoV-2 S1 IgG antibodies were measured with ELISA. The response to the BNT162b2 vaccine was tested by measuring the levels and avidity of SARS-CoV-2 S1 IgG antibodies on D21. The participants were divided into two groups, unexposed and exposed, based on the D0 SARS-CoV-2 antibody results. No significant correlation was found between the levels of 25(OH)D or retinol and the levels, avidity, or fold increase of antibodies in both groups. Similarly, no significant difference in antibody response was found between 25(OH)D status groups, retinol status groups, or combined status groups. These findings show that the baseline vitamin D or vitamin A levels have no effect on the short-term response to a single dose of BNT162b2 vaccine.
Keywords: COVID-19; immune response; vaccine; vitamin A; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Age and vitamin D affect the magnitude of the antibody response to the first dose of the SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine.Curr Res Transl Med. 2022 Jul;70(3):103344. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2022.103344. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Curr Res Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35390564 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world serological responses to extended-interval and heterologous COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in frail, older people (UNCoVER): an interim report from a prospective observational cohort study.Lancet Healthy Longev. 2022 Mar;3(3):e166-e175. doi: 10.1016/S2666-7568(22)00012-5. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2022. PMID: 35224524 Free PMC article.
-
No Significant Association between 25-OH Vitamin D Status and SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response after COVID-19 Vaccination in Nursing Home Residents and Staff.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Aug 8;11(8):1343. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11081343. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631911 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 IgG Spike antibody levels and avidity in natural infection or following vaccination with mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2 vaccines.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Aug 1;19(2):2215677. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2215677. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37264688 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody titres 3 months post-vaccination with the second dose of BNT162b2 vaccine: a longitudinal observational cohort study in western Greece.BMJ Open. 2022 May 19;12(5):e057084. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-057084. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 35589363 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A scoping review: the impact of nutritional status on the efficacy, effectiveness, and immunogenicity of COVID-19 vaccines.Trop Dis Travel Med Vaccines. 2025 Jul 15;11(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40794-025-00258-z. Trop Dis Travel Med Vaccines. 2025. PMID: 40660410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcifediol boosts efficacy of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine by upregulating genes promoting memory T cell responses.NPJ Vaccines. 2024 Jun 20;9(1):114. doi: 10.1038/s41541-024-00909-w. NPJ Vaccines. 2024. PMID: 38902265 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D: A Nutraceutical Supplement at the Crossroad Between Respiratory Infections and COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 12;26(6):2550. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062550. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141190 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 9 August 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Silver Spring (MD): Food and Drug Administration (US) Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Emergency Use Authorizations (EUAs) [(accessed on 9 August 2023)]; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570900/ - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

