Global Burden of Lumpy Skin Disease, Outbreaks, and Future Challenges
- PMID: 37766268
- PMCID: PMC10535115
- DOI: 10.3390/v15091861
Global Burden of Lumpy Skin Disease, Outbreaks, and Future Challenges
Abstract
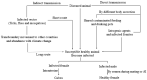
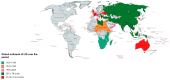
Lumpy skin disease (LSD), a current global concern, causes economic devastation in livestock industries, with cattle and water buffalo reported to have higher morbidity and lower mortality rates. LSD is caused by lumpy skin disease virus (LSDV), a member of the Poxviridae family. It is an enzootic, rapidly explorative and sometimes fatal infection, characterized by multiple raised nodules on the skin of infected animals. It was first reported in Zambia in 1929 and is considered endemic in Africa south of the Sahara desert. It has gradually spread beyond Africa into the Middle East, with periodic occurrences in Asian and East European countries. Recently, it has been spreading in most Asian countries including far East Asia and threatens incursion to LSD-free countries. Rapid and accurate diagnostic capabilities, virus identification, vaccine development, vector control, regional and international collaborations and effective biosecurity policies are important for the control, prevention, and eradication of LSD infections. This review critically evaluates the global burden of LSD, the chronological historical outbreaks of LSD, and future directions for collaborative global actions.
Keywords: economic impact; global biosecurity challenges; historical outbreak; lumpy skin disease; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Das M., Chowdhury M.S.R., Akter S., Mondal A.K., Uddin M.J., Rahman M.M., Rahman M.M. An Updated Review on Lumpy Skin Disease: Perspective of Southeast Asian Countries. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Exp. Ther. 2021;4:322–333. doi: 10.5455/jabet.2021.d133. - DOI
-
- Yilmaz H. Lumpy Skin Disease: Global and Turkish Perspectives. Approaches Poult. Dairy Vet. Sci. 2017;1:11–15. doi: 10.31031/APDV.2017.01.000504. - DOI
-
- Organização Mundial de Saúde . World Health Statistics 2022 (Monitoring Health of the SDGs) World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2022.
-
- Pandey N., Hopker A., Prajapati G., Rahangdale N., Gore K., Sargison N. Observations on Presumptive Lumpy Skin Disease in Native Cattle and Asian Water Buffaloes around the Tiger Reserves of the Central Indian Highlands. New Zealand Vet. J. 2022;70:101–108. doi: 10.1080/00480169.2021.1984335. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources