Hepatitis B Virus Epsilon (ε) RNA Element: Dynamic Regulator of Viral Replication and Attractive Therapeutic Target
- PMID: 37766319
- PMCID: PMC10534774
- DOI: 10.3390/v15091913
Hepatitis B Virus Epsilon (ε) RNA Element: Dynamic Regulator of Viral Replication and Attractive Therapeutic Target
Abstract
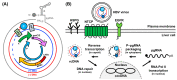
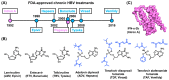
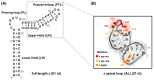
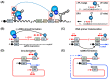
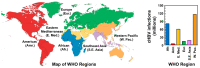
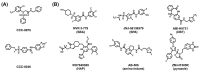
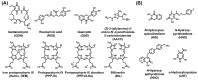
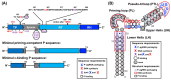
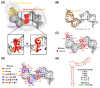
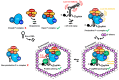
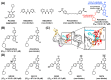
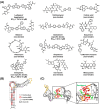
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) chronically infects millions of people worldwide, which underscores the importance of discovering and designing novel anti-HBV therapeutics to complement current treatment strategies. An underexploited but attractive therapeutic target is ε, a cis-acting regulatory stem-loop RNA situated within the HBV pregenomic RNA (pgRNA). The binding of ε to the viral polymerase protein (P) is pivotal, as it triggers the packaging of pgRNA and P, as well as the reverse transcription of the viral genome. Consequently, small molecules capable of disrupting this interaction hold the potential to inhibit the early stages of HBV replication. The rational design of such ligands necessitates high-resolution structural information for the ε-P complex or its individual components. While these data are currently unavailable for P, our recent structural elucidation of ε through solution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy marks a significant advancement in this area. In this review, we provide a brief overview of HBV replication and some of the therapeutic strategies to combat chronic HBV infection. These descriptions are intended to contextualize our recent experimental efforts to characterize ε and identify ε-targeting ligands, with the ultimate goal of developing novel anti-HBV therapeutics.
Keywords: HBV; RNA; small molecules; structure; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RNA-Binding Motif Protein 24 (RBM24) Is Involved in Pregenomic RNA Packaging by Mediating Interaction between Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase and the Epsilon Element.J Virol. 2019 Mar 5;93(6):e02161-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02161-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30626666 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual Screening of Hepatitis B Virus Pre-Genomic RNA as a Novel Therapeutic Target.Molecules. 2023 Feb 14;28(4):1803. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041803. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838792 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Helicase DDX17 Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Blocking Viral Pregenomic RNA Encapsidation.J Virol. 2021 Sep 9;95(19):e0044421. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00444-21. Epub 2021 Sep 9. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34287051 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects for inhibiting the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in hepatitis B virus.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 7;20(25):7993-8004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.7993. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25009369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and function of the encapsidation signal of hepadnaviridae.J Viral Hepat. 1998 Nov;5(6):357-67. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2893.1998.00124.x. J Viral Hepat. 1998. PMID: 9857345 Review.
Cited by
-
Applications of CRISPR/Cas as a Toolbox for Hepatitis B Virus Detection and Therapeutics.Viruses. 2024 Oct 2;16(10):1565. doi: 10.3390/v16101565. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39459899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective [9-15N] Guanosine for Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies of Large Ribonucleic Acids.Chembiochem. 2025 Jun 16;26(12):e202500206. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202500206. Epub 2025 May 23. Chembiochem. 2025. PMID: 40320375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Charnay P., Mandart E., Hampe A., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Galibert F. Localization on the viral genome and nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the two major polypeptides of the Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBs Ag) Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;7:335–346. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.2.335. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

