Prognostic impact of miR-125b and miR-155b and their relationship with MYC and TP53 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: cell-of-origin classification matters
- PMID: 37766562
- PMCID: PMC10628825
- DOI: 10.3960/jslrt.23009
Prognostic impact of miR-125b and miR-155b and their relationship with MYC and TP53 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: cell-of-origin classification matters
Abstract
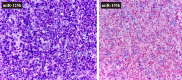
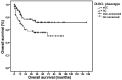
Tumoral microRNAs, such as miR-125b and miR-155b, are important gene expression regulators with complex pathogenetic mechanisms. However, their role in DLBCL, especially when cell-of-origin classification is considered, are still to be elucidated. In a series of 139 DLBCL cases considering germinal center (GC) versus nonGC subtypes, we investigated miR-125b and miR-155b expression by in situ hibridization and their association with some immunophenotypic presentations, including MYC, BCL2 and TP53 expression, MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 translocation status, as well as clinicopathological features and outcomes. miR-125b detection was positively correlated to the Ki-67 index (P = 0.035) in the nGC. Considering the GC subgroup, the percentage of miR-125b positive cells was also correlated to either MYC and MYC/BCL2 double expression (P = 0.047 and P = 0.049, respectively). When it comes to nGC patients, miR-155b percentage and intensity, as well as Allred score, were positively correlated to disease progression (P = 0.038, P = 0.057 and P = 0.039, respectively). In a multivariate analysis, GC phenotype was a significant independent factor associated with higher OS (P = 0.007) and, considering the nGC group, although not significant, the expression of TP53, miR-125b and miR-155b seems to be potential prognostic biomarkers in these tumors. This study demonstrated different pathways based on cell-of-origin classification and highlighted different clinical outcomes. miR-125b, miR-155b and TP53 expression may also represent potential prognostic factors in nGC-DLBCL.
Keywords: MYC; TP53; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; miR-125b; miR-155b.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Significance of BCL2, C-MYC, and BCL6 Genetic Abnormalities, Epstein-Barr Virus Infection, CD5 Protein Expression, Germinal Center B Cell/Non-Germinal Center B-Cell Subtypes, Co-expression of MYC/BCL2 Proteins and Co-expression of MYC/BCL2/BCL6 Proteins in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Clinical and Pathological Correlation Study of 120 Patients.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Apr 20;16(4):556-566. doi: 10.7150/ijms.27610. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31171907 Free PMC article.
-
EZH2 expression is dependent on MYC and TP53 regulation in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.APMIS. 2020 Apr;128(4):308-315. doi: 10.1111/apm.13029. Epub 2020 Feb 27. APMIS. 2020. PMID: 31991488
-
Clinical significance of 'double-hit' and 'double-expression' lymphomas.J Clin Pathol. 2020 Mar;73(3):126-138. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2019-206199. Epub 2019 Oct 15. J Clin Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31615842
-
The Spectrum of MYC Alterations in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.Acta Haematol. 2020;143(6):520-528. doi: 10.1159/000505892. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Acta Haematol. 2020. PMID: 32074595 Review.
-
Should We Use Cell of Origin and Dual-protein Expression in Treating DLBCL?Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Feb;18(2):91-97. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2017.12.003. Epub 2017 Dec 24. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018. PMID: 29352717 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of Action of circRNA/miRNA Network in DLBCL.Noncoding RNA. 2025 Mar 4;11(2):22. doi: 10.3390/ncrna11020022. Noncoding RNA. 2025. PMID: 40126346 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ma XB, Zheng Y, Yuan HP, Jiang J, Wang YP. CD43 expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: CD43 is a marker of adverse prognosis. Hum Pathol. 2015; 46: 593-599. - PubMed
-
- Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood. 2004; 103: 275-282. - PubMed
-
- Neves Filho EH, Hirth CG, Frederico IA, et al. EZH2 expression is dependent on MYC and TP53 regulation in diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma. APMIS. 2020; 128: 308-315. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous