Guideline-discordant inhaler regimens after COPD hospitalization: associations with rurality, drive time to care, and fragmented care - a United States cohort study
- PMID: 37766800
- PMCID: PMC10520452
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lana.2023.100597
Guideline-discordant inhaler regimens after COPD hospitalization: associations with rurality, drive time to care, and fragmented care - a United States cohort study
Abstract
Background: Many patients receive guideline-discordant inhaler regimens after chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) hospitalization. Geography and fragmented care across multiple providers likely influence prescription of guideline-discordant inhaler regimens, but these have not been comprehensively studied. We assessed patient-level differences in guideline-discordant inhaler regimens by rurality, drive time to pulmonary specialty care, and fragmented care.
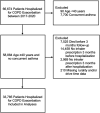
Methods: Retrospective cohort analysis using national Veterans Health Administration (VA) data among patients who received primary care and prescriptions from the VA. Patients hospitalized for COPD exacerbation between 2017 and 2020 were assessed for guideline-discordant inhaler regimens in the subsequent 3 months. Guideline-discordant inhaler regimens were defined as short-acting inhaler/s only, inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) monotherapy, long-acting beta-agonist (LABA) monotherapy, ICS + LABA, long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) monotherapy, or LAMA + ICS. Rural residence and drive time to the closest pulmonary specialty care were obtained from geocoded addresses. Fragmented care was defined as hospitalization outside the VA. We used multivariable logistic regression models to assess associations between rurality, drive time, fragmentated care, and guideline-discordant inhaler regimens. Models were adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, Charlson Comorbidity Index, Area Deprivation Index, and region.
Findings: Of 33,785 patients, 16,398 (48.6%) received guideline-discordant inhaler regimens 3 months after hospitalization. Rural residents had higher odds of guideline-discordant inhalers regimens compared to their urban counterparts (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.18 [95% CI: 1.12-1.23]). The odds of receiving guideline-discordant inhaler regimens increased with longer drive time to pulmonary specialty care (aOR 1.38 [95% CI: 1.30-1.46] for drive time >90 min compared to <30 min). Fragmented care was also associated with higher odds of guideline-discordant inhaler regimens (aOR 1.56 [95% CI: 1.48-1.63]).
Interpretation: Rurality, long drive time to care, and fragmented care were associated with greater prescription of guideline-discordant inhaler regimens after COPD hospitalization. These findings highlight the need to understand challenges in delivering evidence-based care.
Funding: NIHNCATS grants KL2TR002492 and UL1TR002494.
Keywords: Access to care; Drive time to care; Health care disparity; Rural health; Veterans affairs.
Conflict of interest statement
AKB reported grants from the National Institutes of Health. CHS reported grants from the Health Resources and Services Administration, Federal Office of Rural Health Policy, the National Institutes of Health and the CDC; payment or honoraria from Iowa Primary Care Association, Southern Gerontological Society, and the University of Michigan; and leadership or fiduciary role in the National Rural Health Association Board of Trustees. KMK reported personal fees from Nuvaira and Organicell (Data and Safety Monitoring Boards) outside of this work; consulting fees from Allergan/AbbVie and leadership or fiduciary role in the American Thoracic Society Proposal Review Committee, the American Thoracic Society Clinical Problems, and the Assembly Planning Committee.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

