Protective Effects of 2-Methoxyestradiol on Acute Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Injury in Rats
- PMID: 37766820
- PMCID: PMC10520946
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.101787
Protective Effects of 2-Methoxyestradiol on Acute Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Injury in Rats
Abstract
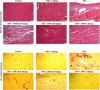
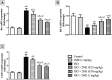
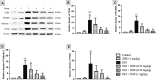
Myocardial injury (MI) is an important pathological driver of mortality worldwide., and arises as a result of imbalances between myocardial oxygen demand and supply. In MI, oxidative stress often leads to inflammatory changes and apoptosis. Current therapies for MI are known to cause various adverse effects. Consequently, the development of new therapeutic agents with a reduced adverse event profile is necessary. In this regard, 2-methoxyestradiol (2ME), the metabolic end-product of oestradiol, possesses anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. The aim of this research is to assess the impact of 2ME on cardiac injury caused by isoproterenol (ISO) in rats. Animals were separated into six groups; controls, and those receiving 2ME (1 mg/kg), ISO (85 mg/kg), ISO + 2ME (0.25 mg/kg), ISO + 2ME (0.5 mg/kg), and ISO + 2ME (1 mg/kg). 2ME significantly attenuated ISO-induced changes in electrocardiographic changes and the cardiac histological pattern. This compound also decreased lactate dehydrogenase activity, creatine kinase myocardial band and troponin levels. The ability of 2ME to act as an antioxidant was shown by a decrease in malondialdehyde concentration, and the restoration of glutathione levels and superoxide dismutase activity. Additionally, 2ME antagonized inflammation and cardiac cell apoptosis, a process determined to be mediated, at least partially, by suppression of Gal-3/TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. 2ME offers protection against acute ISO-induced MI in rats and offers a novel therapeutic management option.
Keywords: 2-Methoxyestradiol (2ME); Inflammation; Isoproterenol (ISO); Myocardial Injury (MI); Oxidative Stress.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Kampeferol protects against oxidative stress and apoptotic damage in experimental model of isoproterenol-induced cardiac toxicity in rats.Phytomedicine. 2016 Nov 15;23(12):1401-1408. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.07.015. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Phytomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27765360
-
Cardioprotective Effect of Taxifolin against Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Injury through Decreasing Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Cell Death, and Activating Nrf2/HO-1 in Mice.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 23;12(11):1546. doi: 10.3390/biom12111546. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36358896 Free PMC article.
-
Nerolidol attenuates isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial infarction in rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022 Mar;395(3):353-363. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02202-w. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35050389
-
Bergapten mediated inflammatory and apoptosis through AMPK/eNOS/AKT signaling pathway of isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in Wistar rats.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2022 Sep;36(9):e23143. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23143. Epub 2022 Jul 11. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35815753
-
Baicalein Ameliorates Myocardial Ischemia Through Reduction of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Apoptosis via TLR4/MyD88/MAPKS/NF-κB Pathway and Regulation of Ca2+ Homeostasis by L-type Ca2+ Channels.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 16;13:842723. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.842723. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35370644 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cardioprotective Effects of Ursodeoxycholic Acid in Isoprenaline-Induced Myocardial Injury in Rats.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 26;14(10):1214. doi: 10.3390/biom14101214. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456147 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects of White Grape Pomace Polyphenols on Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Infarction.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 26;26(5):2035. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052035. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076654 Free PMC article.
-
Icariin inhibits cisplatin-induced ovarian toxicity via modulating NF-κB and PTEN/AKT/mTOR/AMPK axis.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Feb;398(2):1949-1959. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03395-y. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39212737
-
Liraglutide Protects Cardiomyocytes against Isoprenaline-Induced Apoptosis in Experimental Takotsubo Syndrome.Biomedicines. 2024 May 29;12(6):1207. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061207. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-naim A.B., Neamatallah T., Eid B.G., Esmat A., Alamoudi A.J., El-aziz G.S.A., Ashour O.M. 2-methoxyestradiol attenuates testosterone-induced benign prostate hyperplasia in rats through inhibition of HIF-1 α / TGF- β / Smad2 axis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018;2018:4389484. doi: 10.1155/2018/4389484. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Afrasiabi F., Molazem Z., Mani A., Abdi Ardekani A. The effect of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and cardiac chest pain management training on perceived control, depression, stress and anxiety in the spouses of the patients with myocardial infarction: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Community Based Nurs. Midwifery. 2020;8 doi: 10.30476/ijcbnm.2020.81315.0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Taweel A.M., Raish M., Perveen S., Fawzy G.A., Ahmad A., Ansari M.A., Mudassar S., Ganaie M.A. Nepeta deflersiana attenuates isoproterenol-induced myocardial injuries in rats: Possible involvement of oxidative stress, apoptosis, inflammation through nuclear factor (NF)-κB downregulation. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2017;34:67–75. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2017.08.003. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

