The genome sequence of the Dark Spectacle, Abrostola triplasia (Linnaeus, 1758)
- PMID: 37766851
- PMCID: PMC10521094
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.19624.1
The genome sequence of the Dark Spectacle, Abrostola triplasia (Linnaeus, 1758)
Abstract
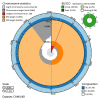
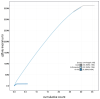
We present a genome assembly from an individual male Abrostola triplasia (the Dark Spectacle; Arthropoda; Insecta; Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). The genome sequence is 362.7 megabases in span. Most of the assembly is scaffolded into 31 chromosomal pseudomolecules, including the Z sex chromosome. The mitochondrial genome has also been assembled and is 15.34 kilobases in length. Gene annotation of this assembly on Ensembl identified 11,532 protein coding genes.
Keywords: Abrostola triplasia; Dark Spectacle; Lepidoptera; chromosomal; genome sequence.
Copyright: © 2023 Boyes D et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The genome sequence of the spectacle, Abrostola tripartita Hufnagel, 1766.Wellcome Open Res. 2021 Dec 6;6:330. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.17355.1. eCollection 2021. Wellcome Open Res. 2021. PMID: 35071799 Free PMC article.
-
The genome sequence of the Burnished Brass, Diachrysia chrysitis (Linnaeus, 1758).Wellcome Open Res. 2023 Feb 15;8:82. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.18990.1. eCollection 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2023. PMID: 37484482 Free PMC article.
-
The genome sequence of the Dark Arches Apamea monoglypha (Hufnagel, 1766).Wellcome Open Res. 2023 Feb 8;8:63. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.18947.1. eCollection 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2023. PMID: 39129913 Free PMC article.
-
The genome sequence of the Hebrew Character, Orthosia gothica (Linnaeus, 1758).Wellcome Open Res. 2024 Feb 19;9:90. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.20904.1. eCollection 2024. Wellcome Open Res. 2024. PMID: 39429633 Free PMC article.
-
The genome sequence of the Small Angle Shades, Euplexia lucipara (Linnaeus, 1758).Wellcome Open Res. 2023 Nov 9;8:509. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.20242.1. eCollection 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2023. PMID: 39193090 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

