Effect of indocyanine green near-infrared light imaging technique guided lymph node dissection on short-term clinical efficacy of minimally invasive radical gastric cancer surgery: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 37766867
- PMCID: PMC10520705
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1257585
Effect of indocyanine green near-infrared light imaging technique guided lymph node dissection on short-term clinical efficacy of minimally invasive radical gastric cancer surgery: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: In recent years, the utilization of indocyanine green near-infrared (ICG NIR) light imaging-guided lymph node dissection in the context of minimally invasive radical gastric cancer has emerged as a novel avenue for investigation. The objective of this study was to assess the influence of employing this technique for guiding lymph node dissection on the short-term clinical outcomes of minimally invasive radical gastric cancer surgery.
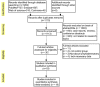
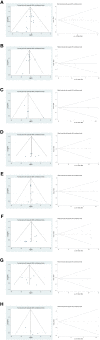
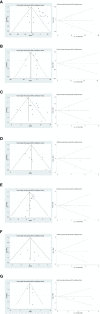
Methods: The present study conducted a comprehensive search for short-term clinical outcomes, comparing the group undergoing ICG NIR light imaging-guided lymph node dissection with the control group, by thoroughly examining relevant literature from the inception to July 2023 in renowned databases such as PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library. The primary endpoints encompassed postoperative complications, including abdominal infection, abdominal bleeding, pneumonia, anastomotic fistula, and overall incidence of complications (defined as any morbidity categorized as Clavien-Dindo class I or higher within 30 days post-surgery or during hospitalization). Additionally, secondary outcome measures consisted of the time interval until the initiation of postoperative gas and food intake, as well as various other parameters, namely postoperative hospital stay, operative time, intraoperative blood loss, total number of harvested lymph nodes, and the number of harvested metastatic lymph nodes. To ensure methodological rigor, the Cochrane Collaboration Risk of Bias Tool and the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) were employed to assess the quality of the included studies, while statistical analyses were performed using Review Manager 5.4 software and Stata, version 12.0 software.
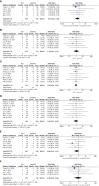
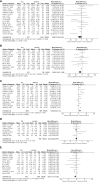
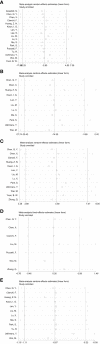
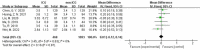
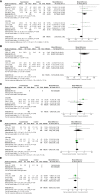
Results: A total of 19 studies including 3103 patients were ultimately included (n=1276 in the ICG group and n=1827 in the non-ICG group). In this meta-analysis, the application of ICG near-infrared light imaging in minimally invasive radical gastric cancer surgery effectively improved the occurrence of postoperative Clavien-Dindo grade II or higher complications in patients (RR=0.72, 95% CI 0.52 to 1.00) with a statistically significant P=0.05; in reducing intraoperative blood loss and shortening While reducing intraoperative blood loss and shortening postoperative hospital stay, it could ensure the thoroughness of lymph node dissection in minimally invasive radical gastric cancer surgery (MD=5.575, 95% CI 3.677-7.473) with significant effect size (Z=5.76, p<0.00001).
Conclusion: The utilization of indocyanine green near-infrared light imaging technology in the context of minimally invasive radical gastric cancer surgery demonstrates notable efficacy in mitigating the occurrence of postoperative complications surpassing Clavien-Dindo grade II, while concurrently augmenting both the overall quantity of lymph node dissections and the identification of positive lymph nodes, all the while ensuring the preservation of surgical safety. Furthermore, the implementation of this technique proves particularly advantageous in the realm of robotic-assisted radical gastric cancer surgery, thus bearing significance for enhancing the short-term prognostic outcomes of patients.
Keywords: gastric cancer resection; indocyanine green; laparoscopy; lymph node dissection; robotics.
Copyright © 2023 Niu, Liu, Li, Sheng, Zhang, Li, Zhao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Diagnostic value of optical imaging combined with indocyanine green-guided sentinel lymph node biopsy in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Dec 25;22(12):1196-1204. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0274.2019.12.017. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31874538 Chinese.
-
Safety and efficacy of indocyanine green near-infrared fluorescent imaging-guided lymph nodes dissection during radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 16;12:917541. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.917541. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36052237 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Indocyanine Green Tracer-Guided Lymph Node Dissection During Laparoscopic Radical Gastrectomy in Patients With Gastric Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Surg. 2020 Apr 1;155(4):300-311. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.6033. JAMA Surg. 2020. PMID: 32101269 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of indocyanine green tracer-guided lymph node dissection in minimally invasive radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 5;12:884011. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.884011. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35992827 Free PMC article.
-
Application value of indocyanine green fluorescence imaging in guiding sentinel lymph node biopsy diagnosis of gastric cancer: Meta-analysis.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024 Jun 27;16(6):1883-1893. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i6.1883. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024. PMID: 38983339 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Indocyanine green and near-infrared fluorescence-guided surgery for gastric cancer: a narrative review.J Minim Invasive Surg. 2024 Dec 15;27(4):185-197. doi: 10.7602/jmis.2024.27.4.185. J Minim Invasive Surg. 2024. PMID: 39675751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyanine dyes in the mitochondria-targeting photodynamic and photothermal therapy.Commun Chem. 2024 Aug 13;7(1):180. doi: 10.1038/s42004-024-01256-6. Commun Chem. 2024. PMID: 39138299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of the 5:2 Diet on Weight Loss and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Overweight and/or Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Endocrinol. 2025 Feb 24;2025:6658512. doi: 10.1155/ije/6658512. eCollection 2025. Int J Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40041761 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yuan Q, Deng D, Pan C, Ren J, Wei T, Wu Z, et al. . Integration of transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics data to reveal HER2-associated metabolic heterogeneity in gastric cancer with response to immunotherapy and neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Front Immunol (2022) 13:951137. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.951137 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kitano S, Iso Y, Moriyama M, Sugimachi K. Laparoscopy-assisted billroth I gastrectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc (1994) 4(2):146–8. - PubMed
-
- Katai H, Mizusawa J, Katayama H, Morita S, Yamada T, Bando E, et al. . Survival outcomes after laparoscopy-assisted distal gastrectomy versus open distal gastrectomy with nodal dissection for clinical stage IA or IB gastric cancer (JCOG0912): a multicentre, non-inferiority, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol (2020) 5(2):142–51. doi: 10.1016/s2468-1253(19)30332-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

