Current Practice Trends in Knee Arthroplasty in India Among ISHKS Members: ISHKS Annual Meeting 2019
- PMID: 37766959
- PMCID: PMC10519882
- DOI: 10.1007/s43465-023-00940-4
Current Practice Trends in Knee Arthroplasty in India Among ISHKS Members: ISHKS Annual Meeting 2019
Abstract
Aim: To assess the current practice trends in knee arthroplasty in India among ISHKS members.
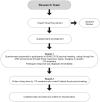
Methods: Literature review on 12 areas of key interest in total knee arthroplasty was conducted. Twenty-eight questions pertaining to these key areas in total knee arthroplasty surgery were presented to the delegates for a physical voting with audience response system (ARS) at ISHKS meeting, Bangalore, 2019. The members who could not attend the meeting voted by an online monkey survey. All questions were given three responses: a. Agree, b. Disagree, and c. Abstain.
Results: 310 delegates participated and 295 voted in the physical meeting and 110 voted online. Consensus was reached for 28 statements representing five domains on the best practices. Overall, 92% of statements reached unanimous or strong consensus. The statements that achieved strong majority (> 90%) were the factors on pre-operative skin preparations, administration of antibiotics 30 min prior skin incision, and current practices of bilateral TKR. Furthermore, there was strong consensus approval on the role of aspirin for prophylaxis of DVT, lack of benefit on use of drain, considerations for pre-emptive analgesia, and neuraxial anesthesia. Finally, there were disparate views and weak consensus on use of laminar airflow theaters and use of surgical space suits, length of antibiotic administration postoperatively, and linking of DVT with PE and death.
Conclusion: This study gives the surgeon practice preferences in knee arthroplasty in India and assists in clinical decision-making for all healthcare professionals.
Keywords: Best clinical practices; Consensus; Knee arthroplasty; Practice guidelines; Practice trends; Total knee replacement.
© Indian Orthopaedics Association 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
International, consensus-based, indications and treatment options for knee arthroplasty in acute fractures around the knee.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2025 Feb 1;145(1):154. doi: 10.1007/s00402-025-05755-6. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2025. PMID: 39891727 Review.
-
ISHKS joint registry: A preliminary report.Indian J Orthop. 2013 Sep;47(5):505-9. doi: 10.4103/0019-5413.118208. Indian J Orthop. 2013. PMID: 24133312 Free PMC article.
-
Recommendations for resuming elective hip and knee arthroplasty in the setting of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: the European Hip Society and European Knee Associates Survey of Members.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020 Sep;28(9):2723-2729. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-06212-0. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020. PMID: 32809121 Free PMC article.
-
Anesthesia and Analgesia Practices in Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Survey of the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons Membership.J Arthroplasty. 2019 Dec;34(12):2872-2877.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2019.06.055. Epub 2019 Jul 8. J Arthroplasty. 2019. PMID: 31371038
-
Consensus statement on unicompartmental knee replacement: A collaboration between BASK and EKS.Knee. 2023 Mar;41:391-396. doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2023.03.015. Knee. 2023. PMID: 37088518
References
-
- Hooper GJ, Rothwell AG, Frampton C, Wyatt MC. Does the use of laminar flow and space suits reduce early deep infection after total hip and knee replacement?: The ten-year results of the New Zealand Joint Registry. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery British. 2011;93(1):85–90. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.93B1.24862,PMID21196549. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xu K. Preoperative chlorhexidine reduces the incidence of surgical site infections in total knee and hip arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Surgery. 2017;39:221.e228222. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources