Bayesian multivariate genetic analysis improves translational insights
- PMID: 37766997
- PMCID: PMC10520309
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107854
Bayesian multivariate genetic analysis improves translational insights
Abstract
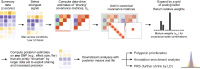
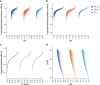
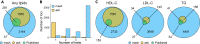
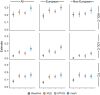
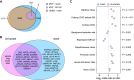
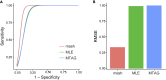
While lipid traits are known essential mediators of cardiovascular disease, few approaches have taken advantage of their shared genetic effects. We apply a Bayesian multivariate size estimator, mash, to GWAS of four lipid traits in the Million Veterans Program (MVP) and provide posterior mean and local false sign rates for all effects. These estimates borrow information across traits to improve effect size accuracy. We show that controlling local false sign rates accurately and powerfully identifies replicable genetic associations and that multivariate control furthers the ability to explain complex diseases. Our application yields high concordance between independent datasets, more accurately prioritizes causal genes, and significantly improves polygenic prediction beyond state-of-the-art methods by up to 59% for lipid traits. The use of Bayesian multivariate genetic shrinkage has yet to be applied to human quantitative trait GWAS results, and we present a staged approach to prediction on a polygenic scale.
Keywords: Association analysis; Biocomputational method; Computational bioinformatics; Genomic analysis; Human genetics.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
C.J.O. is an employee of Novartis. P.N. reports research grants from Allelica, Apple, Amgen, Boston Scientific, Genentech/Roche, and Novartis, personal fees from Allelica, Apple, AstraZeneca, Blackstone Life Sciences, Eli Lilly & Co, Foresite Labs, Genentech/Roche, GV, HeartFlow, Magnet Biomedicine, and Novartis, scientific advisory board membership of Esperion Therapeutics, Preciseli, and TenSixteen Bio, scientific co-founder of TenSixteen Bio, equity in MyOme, Preciseli, and TenSixteen Bio, and spousal employment at Vertex Pharmaceuticals, all unrelated to the present work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multivariate genome-wide associations for immune traits in two maternal pig lines.BMC Genomics. 2023 Aug 28;24(1):492. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09594-w. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37641029 Free PMC article.
-
A Multiple-Trait Bayesian Lasso for Genome-Enabled Analysis and Prediction of Complex Traits.Genetics. 2020 Feb;214(2):305-331. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302934. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Genetics. 2020. PMID: 31879318 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient weighting methods for genomic best linear-unbiased prediction (BLUP) adapted to the genetic architectures of quantitative traits.Heredity (Edinb). 2021 Feb;126(2):320-334. doi: 10.1038/s41437-020-00372-y. Epub 2020 Sep 26. Heredity (Edinb). 2021. PMID: 32980863 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of shared genomic loci using the conditional false discovery rate approach.Hum Genet. 2020 Jan;139(1):85-94. doi: 10.1007/s00439-019-02060-2. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 31520123 Review.
-
Genetics of complex traits: prediction of phenotype, identification of causal polymorphisms and genetic architecture.Proc Biol Sci. 2016 Jul 27;283(1835):20160569. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2016.0569. Proc Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27440663 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

