Comparisons of the effects of solute interactions on partition coefficient, k D, in selected binary immiscible solvents: a case of oxalic acid and succinic acid
- PMID: 37767079
- PMCID: PMC10521093
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.55200.1
Comparisons of the effects of solute interactions on partition coefficient, k D, in selected binary immiscible solvents: a case of oxalic acid and succinic acid
Abstract
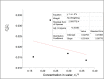
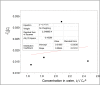
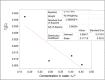
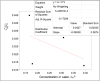
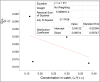
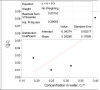
Background: The molecular distributions of solutes in binary immiscible solvents as used in partition coefficient technique serve as measures of the solute separation, concentration and beneficiation from contaminants. Methods: The effects of solute interactions on partition coefficient, k D, in selected binary immiscible solvents were investigated at 30 0C and atmospheric pressure. The activities from the interactions with changes of concentrations within the solvents were analysed. These were done using simple titration method. The solutes were distributed in the binary solvents and the concentrations from the two layers formed were determined by titration method. The interactions of oxalic acid and succinic acid in carbon tetrachloride-water, diethyl ether-water, and n-hexane-water were studied for the partition coefficient values in the respective systems, to determine the nature and degree of the interfering reactions that are affecting the distributions, and to ascertain the best binary solvents from the three systems. Results: Oxalic acid has the partition coefficient of 0.0738 in carbon tetrachloride-water with the dimerization constant of -15.7092 and ionization constant of 0.0303. Oxalic acid has the distribution coefficient of 0.0173, dimerization constant of 144.0167 and the ionization constant of 0.0035 in diethyl ether-water. Oxalic acid has the partition coefficient of 0.0279, dimerization constant of 20.2798 and ionization constant of 0.0019 in n-hexane-water. Succinic acid has the partition coefficient of -0.05617, dimerization constant of -18.5655 and ionization constant of 0.0284 in carbon tetrachloride-water. In diethyl ether-water, succinic acid has the partition coefficient of 0.0427, dimerization constant of -18.1611 and ionization constant of 0.0332. In n-hexane-water, succinic acid has the partition coefficient of -0.04274, dimerization constant of 71.9491 and ionization constant of 0.0265. Conclusion: From these results, carbon tetrachloride-water is recommended for the purification and extraction of oxalic acid from contaminants. Carbon tetrachloride-water is also the best binary immiscible solvent for succinic acid.
Keywords: Binary Solvent; Dimerization; Ionization; Oxalic Acid; Partition Coefficient; Succinic Acid.
Copyright: © 2022 V. O. O et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures












References
-
- Onyeocha VO, Akpan OD, Onuchukwu IA, et al. : The Dimerization Effects of Some Solutes on the Partition Coefficient (k D) in Binary Immiscible Solvents. Intern. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astrono. 2018;80:40–52. 10.18052/www.scipress.com/ILCPA.80.40 Reference Source - DOI
-
- Onuchukwu AI: Chemical Thermodynamics for Science Students. Owerri: FUTO Press; 4th ed. 2016;175.
-
- Rastogi RP, Misra RR: An Introduction to Chemical Thermodynamics. India: Vikas Publishing House Pvt Ltd; Second Edition. 1980; pp296–300.
-
- Staunton S, Geoderma: Sensitivity Analysis of the Distribution Coefficient, k D, of Nickel with Changing Soil Chemical Properties. Oct 2004.
-
- Othmer K: Encyclopaedia of Chemical Technology. 1979; Vol,1: pp147. Third Edition.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

