Survival status and risk factors for mortality among multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: A retrospective follow-up study
- PMID: 37767135
- PMCID: PMC10520522
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jctube.2023.100398
Survival status and risk factors for mortality among multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: A retrospective follow-up study
Abstract
Background: Tuberculosis continues to be a major health concern around the world. It kills an estimated 1.6 million people each year. The World Health Organization (WHO) removed Ethiopia from its list of thirty countries having a high prevalence of MDR/RR-TB in 2021. As a result, the aim of this study was to assess the current context of survival status and risk factors of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, in 2022.
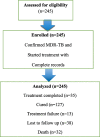
Methods: An institutional-based retrospective cohort study with 245 patients was undertaken using multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients who were recruited from January 1st, 2018 to December 30th, 2021, in St. Peter's specialized hospital. To find independent predictors of survival status, Cox regression analysis was used. An adjusted hazard ratio with a 95% confidence interval and a p-value of < 0.05 was used to establish association and statistical significance.
Results: The result of the study revealed that the incidence of mortality in this study was 13.1% (95% CI: 10.3-16.5). Moreover, being male (AOR = 3.7: 95% CI = 1.2, 11.4), old age (AOR = 14: 95% CI = 3.0, 60.4), site of TB (AOR = 0.2: 95% CI = 0.03, 0.6), and presence of comorbidity (AOR = 9.2: 95% CI = 2.4, 35.3), were independent predictors of time to death.
Conclusion: Generally, the death rate among research participants was high. Moreover, male gender, old age, site of tuberculosis, and presence of other comorbidity were predictors of mortality among MDR-TB patients.
Keywords: Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis; Survival probability; Treatment outcome.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Survival Status and Predictors of Mortality among Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis Patients in Saint Peter's Specialized Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2021 Sep 3;2021:6696199. doi: 10.1155/2021/6696199. eCollection 2021. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34527088 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Time to Death of Patients with Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis at Saint Peter's Specialized Hospital.J Res Health Sci. 2021 May 19;21(2):e00513. doi: 10.34172/jrhs.2021.50. J Res Health Sci. 2021. PMID: 34465635 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse drug reactions and contributing factors in patients with drug-resistant tuberculosis: A 7-year retrospective cohort study in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2025 Mar 5;39:100515. doi: 10.1016/j.jctube.2025.100515. eCollection 2025 May. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2025. PMID: 40161469 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological distress and its effect on tuberculosis treatment outcomes in Ethiopia.Glob Health Action. 2015 Nov 24;8:29019. doi: 10.3402/gha.v8.29019. eCollection 2015. Glob Health Action. 2015. PMID: 26610316 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Knowledge and Attitude of Tuberculosis Patients in Direct Observation Therapy Program towards Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study.Tuberc Res Treat. 2020 Jun 6;2020:6475286. doi: 10.1155/2020/6475286. eCollection 2020. Tuberc Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32566290 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Factors associated with unfavourable treatment outcomes among patients with Multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis receiving outpatients care.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 4;15(1):28335. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13227-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40760140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global tuberculosis report 2022. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
-
- Floyd K., Glaziou P., Zumla A., Raviglione M. The global tuberculosis epidemic and progress in care, prevention, and research: an overview in year 3 of the End TB era. Lancet Respir Med. 2018 Apr 1;6(4):299–314. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. World Health Organization Global Tuberculosis Report 2021. URL: https://www. who. int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tbreports/global-tuberculosis-report-2021. 2021.
-
- Lönnroth K., Jaramillo E., Williams B., Dye C., Raviglione M. Tuberculosis: the role of risk factors and social determinants. Equity, social determinants and public health programmes. 2010;219:241.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials