Pediatric primary intraventricular hemorrhage: A case report of isolated fourth ventricle hemorrhage in a 10-year-old boy
- PMID: 37767151
- PMCID: PMC10520413
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.7952
Pediatric primary intraventricular hemorrhage: A case report of isolated fourth ventricle hemorrhage in a 10-year-old boy
Abstract
Key clinical message: Primary intraventricular hemorrhage (PIVH) is a rare condition in pediatric patients, presenting with headache, vomiting, and altered mental status. Surgical interventions, such as external ventricular drain placement, followed by ventriculoperitoneal shunting, show promising outcomes. Further research is needed to enhance understanding and optimize management strategies for pediatric PIVH.
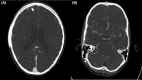
Abstract: This case report describes a 10-year-old boy with isolated primary intraventricular hemorrhage (PIVH) in the fourth ventricle, shedding light on its clinical presentation and management challenges. The patient presented with headache, vomiting, and altered sensorium, and was subsequently diagnosed with obstructive hydrocephalus due to intraventricular bleeding. Emergency external ventricular drain (EVD) insertion was performed, followed by ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement, resulting in a favorable outcome. The etiology of PIVH in children differs from that in adults, with arteriovenous malformations, Moyamoya disease, and aneurysms being commonly implicated causes. Management strategies for pediatric PIVH are challenging due to limited research, but EVD placement and surgical interventions have shown promise.
Keywords: external ventricular drain; pediatric intraventricular hemorrhage; pediatric neurosurgery; ventriculoperitoneal shunt.
© 2023 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Weinstein R, Ess K, Sirdar B, Song S, Cutting S. Primary intraventricular hemorrhage: clinical characteristics and outcomes. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;26(5):995‐999. - PubMed
-
- Guo R, Chen R, Yu Z, et al. Primary intraventricular hemorrhage in pediatric patients: causes, characteristics, and outcomes. World Neurosurg. 2020;133:e121‐e128. - PubMed
-
- Guédon A, Blauwblomme T, Boulouis G, et al. Predictors of outcome in patients with pediatric intracerebral hemorrhage: development and validation of a modified score. Radiology. 2018;286(2):651‐658. - PubMed
-
- Darby DG, Donnan GA, Saling M, Walsh K, Bladin PF. Primary intraventricular hemorrhage: clinical and neuropsychological findings in a prospective stroke series. Neurology. 1988;38(1):68‐75. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

