Broadly applicable methods for the detection of artefacts in electroencephalography acquired simultaneously with hemodynamic recordings
- PMID: 37767154
- PMCID: PMC10520509
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2023.102376
Broadly applicable methods for the detection of artefacts in electroencephalography acquired simultaneously with hemodynamic recordings
Abstract
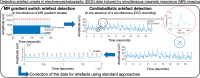
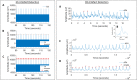
Electroencephalography (EEG) data, acquired simultaneously with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), must be corrected for artefacts related to MR gradient switches (GS) and the cardioballistic (CB) effect. Canonical approaches require additional signal acquisition for artefact detection (e.g., MR volume onsets, ECG), without which the EEG data would be rendered uncleanable from these artefacts.•We present two broadly applicable methods for artefact detection based on peak detection combined with temporal constraints with respect to periodicity directly from the EEG data itself; no additional signals are required. We validated the performance of our methods versus the two canonical approaches for detection of GS/CB artefact, respectively, on 26 healthy human EEG-functional MRI resting-state datasets. Utilising various performance metrics, we found our methods to perform as well as - and sometimes better than - the canonical standard approaches. With as little as one EEG channel recording, our methods can be applied to detect GS/CB artefacts in EEG data acquired simultaneously with MRI in the absence of MR volume onsets and/or an ECG recording. The detected artefact onsets can then be fed into the standard artefact correction software.
Keywords: Artefact; Artifind; Ballistocardiac; Cardioballistic; ECG; EEG-fMRI; Gradient; Pulse.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Unified Retrospective EEG Motion Educated Artefact Suppression for EEG-fMRI to Suppress Magnetic Field Gradient Artefacts During Motion.Brain Topogr. 2021 Nov;34(6):745-761. doi: 10.1007/s10548-021-00870-0. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Brain Topogr. 2021. PMID: 34554373
-
Data-driven beamforming technique to attenuate ballistocardiogram artefacts in electroencephalography-functional magnetic resonance imaging without detecting cardiac pulses in electrocardiography recordings.Hum Brain Mapp. 2021 Aug 15;42(12):3993-4021. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25535. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021. PMID: 34101939 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing the gradient artefact in simultaneous EEG-fMRI by adjusting the subject's axial position.Neuroimage. 2011 Feb 1;54(3):1942-50. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.09.079. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 20932913 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal neuroimaging in humans at 9.4 T: a technological breakthrough towards an advanced metabolic imaging scanner.Brain Struct Funct. 2015 Jul;220(4):1867-84. doi: 10.1007/s00429-014-0843-4. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Brain Struct Funct. 2015. PMID: 25017191 Review.
-
Technical recommendations and interpretation guidelines for electroencephalography for premature and full-term newborns.Neurophysiol Clin. 2021 Jan;51(1):35-60. doi: 10.1016/j.neucli.2020.10.005. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Neurophysiol Clin. 2021. PMID: 33168466 Review.
References
-
- Berger H. Über das Elektrenkephalogramm des Menschen. Archiv. Psychiatr. Nervenkrankh. 1929;87(1):527–570. doi: 10.1007/BF01797193. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

