Positive impact of social relationships fostered by physical and/or cognitive group activity on older people's quality of life: PRISMA systematic review
- PMID: 37767210
- PMCID: PMC10520714
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1166072
Positive impact of social relationships fostered by physical and/or cognitive group activity on older people's quality of life: PRISMA systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: This review identified and examined the research literature on the effect of participating in physical and/or cognitive activities on older people's quality of life, to establish whether the social relationships fostered by these activities can be a vector of better physical, mental and social quality of life.
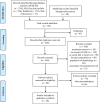
Method: A systematic review of the literature was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. We searched four databases (MEDLINE, APA PsycArticles/PsycInfo, PubMed, and Web of Science) for articles published between 1975 and 2022 using search terms related to psychosocial, population, and intervention topics. Studies were eligible if they involved older adults, participation in at least one activity (physical or cognitive), and at least one quality of life related outcome measure.
Results: We selected 20 articles published between 1990 and 2021, the majority concerning studies conducted in English-speaking countries. Ten studies were interventional (introduction of program of activities), and 10 studies were observational (60% quantitative, 40% qualitative). Overall, results revealed a positive impact of the activities on every aspect of quality of life (i.e., cognitive, physical, social, psychological, and quality of life in general).
Conclusion: The present review confirmed the beneficial impact of practicing physical and/or cognitive group activities on older people's quality of life, but the contribution of social factors and social relationships remains underestimated and not well defined in researches.
Keywords: aging; cognitive activities; physical activities; quality of life; social relations; wellbeing.
Copyright © 2023 Gonnord, Clarys, Boucard and Esnard.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Impact of summer programmes on the outcomes of disadvantaged or 'at risk' young people: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 13;20(2):e1406. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1406. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38873396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
-
Voluntary work for the physical and mental health of older volunteers: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 23;16(4):e1124. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1124. eCollection 2020 Dec. Campbell Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 37016617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How to reduce the adverse effects of weight stigma on the quality of life: a preferred reported items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA).Front Psychol. 2024 Dec 24;15:1421609. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1421609. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39776964 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
How to Cope with Coping in Adult Post-Hemorrhagic Patients Undergoing Neurorehabilitation: A Scoping Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 18;14(14):5121. doi: 10.3390/jcm14145121. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40725813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shared reading interventions to promote psychosocial well-being in older adults: a systematic review.Health Promot Int. 2025 Mar 5;40(2):daaf036. doi: 10.1093/heapro/daaf036. Health Promot Int. 2025. PMID: 40208190 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting Healthy Aging for Older People Living with Chronic Disease by Implementing Community Health Programs: A Randomized Controlled Feasibility Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Dec 13;21(12):1667. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21121667. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39767506 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of Internet Usage on Depression Among Older Adults: Comprehensive Study.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jan 31;27:e65399. doi: 10.2196/65399. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39890098 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of traditional Thai folk dance combined with cognitive stimulation program on behavior and cognition among older adults with cognitive decline: A randomized controlled trial.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025 Apr;12(4):100066. doi: 10.1016/j.tjpad.2025.100066. Epub 2025 Jan 17. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025. PMID: 39824702 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources