Fabrication of Biogenic Titanium Nanoparticles and Investigating Their Biological Properties for Dental Applications
- PMID: 37767269
- PMCID: PMC10521939
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.44209
Fabrication of Biogenic Titanium Nanoparticles and Investigating Their Biological Properties for Dental Applications
Abstract
Introduction: Oral inflammation, often triggered by infections, injuries, or immune responses, can compromise treatment outcomes, delay healing, and contribute to patient discomfort. The development of green nanoparticle synthesis methods is receiving attention due to their potential advantages over existing approaches. These procedures use commonly available, affordable, and environmentally friendly natural plant extracts. Due to their numerous uses in various industries, titanium oxide nanoparticles (TiO2NPs) have attracted the most attention among the nanoparticles. In this study, we present the green synthesis of Myristica fragrans (mace) extract as a reductant and stabilizer for the production of curcumin-functionalized TiO2NPs (CTN). We additionally evaluated the effectiveness of these nanoparticles as anti-inflammatory agents.
Objective: In this study, we aim to develop biogenic TiO2NPs using Myristica fragrans as a natural capping agent and functionalized with curcumin for effectively managing oral inflammation in dental applications.
Methods: The nanoparticles were synthesized using the green synthesis method and characterized using various characterization techniques. Biocompatibility was evaluated using hemolytic assays, and the bioactivity of the nanoparticles was assessed using anti-inflammatory assays.
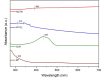
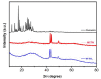
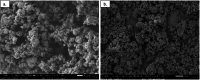
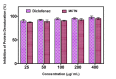
Results: Curcumin-coated M-TiO2NPs (MCTN) were successfully synthesized and characterized by various techniques, confirming their morphology, crystallinity, functionalization, elemental composition, size, and stability. In vitro bioactivity studies revealed that MCTN exhibited significant anti-inflammatory activity, as evidenced by the inhibition of protein denaturation with minimal hemolytic potential. These findings highlight the potential of MCTN as a promising candidate for anti-inflammatory applications.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that MCTN exhibits promising anti-inflammatory and anti-hemolytic properties. However, further in-depth in vivo analysis is required to fully understand their efficacy and toxicity.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; curcumin; green synthesis; myristica fragrans; titanium oxide nanoparticles.
Copyright © 2023, A.S. et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Preparation of Herbal Nano-Formulation-Assisted Mouth Paint Using Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Its Biomedical Applications.Cureus. 2023 Nov 5;15(11):e48332. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48332. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38060706 Free PMC article.
-
Algae-Mediated Green Synthesis of Dextran-Coated Titanium Nanoparticles and Their Cytotoxic Potential Against MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2024 Oct;13(3):358-367. doi: 10.61186/rbmb.13.3.358. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 40330561 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactivities of Ethanolic Extracts of Three Parts (Wood, Nutmeg and Mace) from Myristica fragrans Houtt.J Med Assoc Thai. 2016 Jul;99 Suppl 4:S124-30. J Med Assoc Thai. 2016. PMID: 29926690
-
Revisiting the Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles: Uncovering Influences of Plant Extracts as Reducing Agents for Enhanced Synthesis Efficiency and Its Biomedical Applications.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Aug 18;18:4727-4750. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S419369. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37621852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using plant biomass and their applications- A review.Chemosphere. 2022 Aug;300:134612. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134612. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35430203 Review.
Cited by
-
Facile Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Copper Oxide Nanoneedle Arrays for Practical Biomedical Applications.Cureus. 2024 Jan 4;16(1):e51678. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51678. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38318567 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of Herbal Nano-Formulation-Assisted Mouth Paint Using Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Its Biomedical Applications.Cureus. 2023 Nov 5;15(11):e48332. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48332. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38060706 Free PMC article.
-
Coating Polyetheretherketone Implant Surface With Titanium Oxide Nanoparticles and Hyaluronic Acid: An In Vitro Study.Cureus. 2025 Jan 13;17(1):e77383. doi: 10.7759/cureus.77383. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39944440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Green synthesis of nanoparticles: current developments and limitations. Ying S, Guan Z, Ofoegbu PC, Clubb P, Rico C, He F, Hong J. Environ Technol Innov. 2022;26:102336.
-
- Rane AV, Kanny K, Abitha VK, Thomas S. Synthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing; 2018. Methods for synthesis of nanoparticles and fabrication of nanocomposites; pp. 121–139.
-
- Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles study using clove and cumin and its anti- inflammatory activity. Jayavarsha V, Rajeshkumar S, Lakshmi T, Sulochana G. J Complement Med Res. 2022;13:84.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
