MOF-based stimuli-responsive controlled release nanopesticide: mini review
- PMID: 37767340
- PMCID: PMC10520976
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1272725
MOF-based stimuli-responsive controlled release nanopesticide: mini review
Abstract
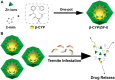
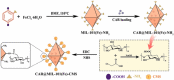
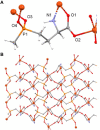
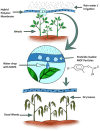
By releasing an adequate amount of active ingredients when triggered by environmental and biological factors, the nanopesticides that respond to stimuli can enhance the efficacy of pesticides and contribute to the betterment of both the environment and food safety. The versatile nature and highly porous structure of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have recently garnered significant interest as drug carriers for various applications. In recent years, there has been significant progress in the development of metal-organic frameworks as nanocarriers for pesticide applications. This review focuses on the advancements, challenges, and potential future enhancements in the design of metal-organic frameworks as nanocarriers in the field of pesticides. We explore the various stimuli-responsive metal-organic frameworks carriers, particularly focusing on zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8), which have been successfully activated by external stimuli such as pH-responsive or multiple stimuli-responsive mechanisms. In conclusion, this paper presents the existing issues and future prospects of metal-organic frameworks-based nanopesticides with stimuli-responsive controlled release.
Keywords: bioactivity; controlled release; metal-organic frameworks; nanopesticide; stimuli-responsive.
Copyright © 2023 Hu, Yan, Fei, Zhang and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Smart controlled-release nanopesticides based on metal-organic frameworks.Chem Commun (Camb). 2024 Jun 11;60(48):6082-6092. doi: 10.1039/d4cc01390e. Chem Commun (Camb). 2024. PMID: 38813806 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Metal-Organic Frameworks as Anticancer Drug Delivery Systems: A Review.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(18):2487-2504. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666210119093844. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33463479 Review.
-
Facile, Smart, and Degradable Metal-Organic Framework Nanopesticides Gated with FeIII-Tannic Acid Networks in Response to Seven Biological and Environmental Stimuli.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 Apr 28;13(16):19507-19520. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c04118. Epub 2021 Apr 15. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 33856772
-
Recent advances in stimuli-response mechanisms of nano-enabled controlled-release fertilizers and pesticides.Eco Environ Health. 2023 Jul 23;2(3):161-175. doi: 10.1016/j.eehl.2023.07.005. eCollection 2023 Sep. Eco Environ Health. 2023. PMID: 38074996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in Metal-Organic Frameworks as nanocarriers for triggered release of anticancer drugs: Brief history, biomedical applications, challenges and future perspective.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2023 May;225:113266. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2023.113266. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2023. PMID: 36947901 Review.
Cited by
-
pH and Pectinase Dual-Responsive Zinc Oxide Core-Shell Nanopesticide: Efficient Control of Sclerotinia Disease and Reduction of Environmental Risks.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Dec 16;14(24):2022. doi: 10.3390/nano14242022. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39728558 Free PMC article.
-
RGD-modified ZIF-8 nanoparticles as a drug carrier for MR imaging and targeted drug delivery in myocardial infarction.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024;19(18-20):1585-1600. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2024.2365623. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39011901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdelhameed R. M., Abdelhameed R. E., Kamel H. A. (2019). Iron-based metal-organic-frameworks as fertilizers for hydroponically grown Phaseolus vulgaris. Mater Lett. 237, 72–79. 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.11.072 - DOI
-
- Anstoetz M., Sharma N., Clark M., Yee L. H. (2016). Characterization of an oxalate-phosphate-amine metal–organic framework (OPA-MOF) exhibiting properties suited for innovative applications in agriculture. J. Mater Sci. 51, 9239–9252. 10.1007/s10853-016-0171-6 - DOI
-
- Applerot G., Lipovsky A., Dror R., Perkas N., Nitzan Y., Lubart R., et al. (2009). Enhanced antibacterial activity of nanocrystalline ZnO due to increased ROS‐mediated cell injury. Adv. Funct. Mater 19 (6), 842–852. 10.1002/adfm.200801081 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

