The role of intravascular imaging in chronic total occlusion percutaneous coronary intervention
- PMID: 37767372
- PMCID: PMC10520251
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1199067
The role of intravascular imaging in chronic total occlusion percutaneous coronary intervention
Abstract
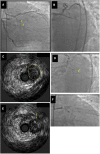
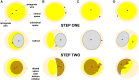
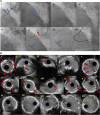
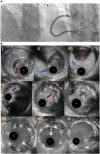
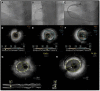
Chronic total occlusions (CTOs) represent the most complex subset of coronary artery disease and therefore careful planning of CTO percutaneous coronary recanalization (PCI) strategy is of paramount importance aiming to achieve procedural success, and improve patient's safety and post CTO PCI outcomes. Intravascular imaging has an essential role in facilitating CTO PCΙ. First, intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), due to its higher penetration depth compared to optical coherence tomography (OCT), and the additional capacity of real-time imaging without need for contrast injection is considered the preferred imaging modality for CTO PCI. Secondly, IVUS can be used to resolve proximal cap ambiguity, facilitate wire re-entry when dissection and re-entry strategies are applied and most importantly to guide stent deployment and optimization post implantation. The role of OCT during CTO PCI is currently limited to stent sizing and optimization, however, due to its high spatial resolution, OCT is ideal for detecting stent edge dissections and strut malapposition. In this review, we describe the use of intravascular imaging for lesion crossing, plaque characterization and wire tracking, extra- or intra-plaque, and stent sizing and optimization during CTO PCI and summarize the findings of the major studies in this field.
Keywords: CTO crossing; chronic total occlusion (CTO); intravascular imaging; intravascular ultrasound (IVUS); optical coherence tomography (OCT); stent optimization.
© 2023 Xenogiannis, Pavlidis, Kaier, Rigopoulos, Karamasis, Triantafyllis, Vardas, Brilakis and Kalogeropoulos.
Conflict of interest statement
EB has received consulting and speaker honoraria from Abbott Vascular, the American Heart Association (associate editor, Circulation), Amgen, Asahi Intecc, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Cardiovascular Innovations Foundation (Board of Directors), ControlRad, Cardiovascular Systems, Inc, Elsevier, GE Healthcare, IMDS, InfraRedx, Medicure, Medtronic, Opsens, Siemens, and Teleflex; is an owner of Hippocrates; and is a shareholder in MHI Ventures and Cleerly Health. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Azzalini L, Carlino M, Bellini B, Marini C, Pazzanese V, Toscano E, et al. Long-term outcomes of chronic total occlusion recanalization versus percutaneous coronary intervention for complex non-occlusive coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. (2020) 125(2):182–8. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.10.034 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Park JJ, Chae IH, Cho YS, Kim SW, Yang HM, Seo JB, et al. The recanalization of chronic total occlusion leads to lumen area increase in distal reference segments in selected patients: an intravascular ultrasound study. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. (2012) 5(8):827–36. 10.1016/j.jcin.2012.05.004 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

