Effect of CO2 and H2 gas mixture in cold water immersion on recovery after eccentric loading
- PMID: 37767470
- PMCID: PMC10520833
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20288
Effect of CO2 and H2 gas mixture in cold water immersion on recovery after eccentric loading
Abstract
Background: The findings of previous studies support the efficacy of cold water immersion (CWI) with carbon dioxide (CO2) in enhancing muscle blood flow and maintaining aerobic performance efficiency. We hypothesize that the addition of hydrogen gas (H2), known for its antioxidant properties and role in inflammation regulation, to C-CWI can enhance recovery after eccentric exercise.
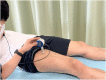
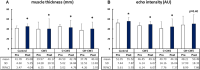
Subjects: and Methods: Thirty-four healthy subjects performed a knee-extensor eccentric exercise. They were randomly allocated into four groups: control, CWI, CO2-rich CWI (C-CWI), and CO2 + H2 gas mixture CWI (CH-CWI). In the three CWI groups, all subjects were immersed in the appropriate bath at 20 °C for 20 min immediately after 60 repetitions of eccentric exercise. Before exercise and after 48 h of recovery, the subjects' maximal voluntary isometric contraction torque (MVC-ISO), maximal voluntary concentric (MVC-CON) contraction torque, countermovement jump (CMJ) height, knee flexion range of motion (ROM), muscle soreness, and muscle thickness were measured.
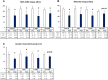
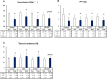
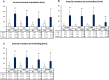
Results: In the CH-CWI group only, the MVC-ISO, CMJ height, and ROM did not decrease significantly post-exercise, whereas all of these decreased in the other three groups. Muscle soreness at palpation, contraction, and stretching significantly increased post-exercise in all groups. Echo intensity and tissue hardness did not increase significantly in the CH-CWI group.
Conclusions: CH-CWI stimulated recovery from impairments in MVC-ISO torque, CMJ height, knee-flexion ROM, tissue hardness, and echo intensity. These findings indicate that CH-CWI can promote recovery after eccentric exercise.
Keywords: Cold water immersion; Eccentric exercise; Hydrogen; Muscle damage.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Masatoshi Nakamura reports financial support was provided by Iwatani Corporation. Yoshiyuki Fukuoka reports financial support was provided by Osaka City Innovation Creation Support Grant.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of cold water immersion and compression garment use after eccentric exercise on recovery.J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2019 Mar 31;23(1):48-54. doi: 10.20463/jenb.2019.0007. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31010274 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery From Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage: Cold-Water Immersion Versus Whole-Body Cryotherapy.Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2017 Mar;12(3):402-409. doi: 10.1123/ijspp.2016-0186. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2017. PMID: 27396361 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of cold-water immersion treatment on recovery from exercise-induced muscle damage in the hamstring.Eur J Sport Sci. 2025 Mar;25(3):e12235. doi: 10.1002/ejsc.12235. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Eur J Sport Sci. 2025. PMID: 39665595 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of cold water immersion after exercise on fatigue recovery and exercise performance--meta analysis.Front Physiol. 2023 Jan 20;14:1006512. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1006512. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36744038 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Cold-Water Immersion Compared with Passive Recovery Following a Single Bout of Strenuous Exercise on Athletic Performance in Physically Active Participants: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis and Meta-regression.Sports Med. 2022 Jul;52(7):1667-1688. doi: 10.1007/s40279-022-01644-9. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 35157264 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pre-Exercise Ingestion of Hydrogen-Rich Cold Water Enhances Endurance Performance and Lactate Response in Heat.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jun 28;61(7):1173. doi: 10.3390/medicina61071173. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40731803 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen-rich water supplementation promotes muscle recovery after two strenuous training sessions performed on the same day in elite fin swimmers: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial.Front Physiol. 2024 Apr 12;15:1321160. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1321160. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38681143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tavares F., et al. Practical Applications of Water Immersion Recovery Modalities for Team Sports. 2018;40:48–60.
-
- Tavares F., Smith T.B., Driller M. Fatigue and recovery in rugby: a review. Sports Med. 2017;47(8):1515–1530. - PubMed
-
- Versey N.G., Halson S.L., Dawson B.T. Water immersion recovery for athletes: effect on exercise performance and practical recommendations. Sports Med. 2013;43(11):1101–1130. - PubMed
-
- Ihsan M., Watson G., Abbiss C.R. What are the physiological mechanisms for post-exercise cold water immersion in the recovery from prolonged endurance and intermittent exercise? Sports Med. 2016;46(8):1095–1109. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

