Clinical relevance of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio combined with APACHEII for prognosis of severe heatstroke
- PMID: 37767493
- PMCID: PMC10520812
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20346
Clinical relevance of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio combined with APACHEII for prognosis of severe heatstroke
Abstract
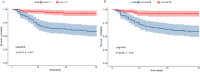
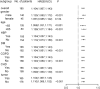
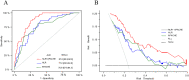
We evaluated clinical implication of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) for severe heatstroke and predictive value of combined acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHEII) score for prognosis of severe heatstroke. Retrospectively, we studied 185 individuals that have been admitted at emergency department for severe heatstroke. On the basis of their prognosis, we sorted the patients into two categories, namely non-survival (n = 43) and survival groups (n = 142). The primary outcome was 30-day mortality. A considerably higher NLR was observed among the non-survivors compared to survivors (P < 0.05). After correction for confounders, statistical analysis using multi-variable Cox regression indicated NLR as an independent risk factor for patient death (HR = 1.167, 95%CI = 1.110-1.226, P < 0.001). Through receiver-operating characteristics (ROC) curve, we estimated area-under the curve (AUC) of NLR to be 0.7720 (95% CI [0.6953, 0.8488]). Also, transformation of NLR into a profile type analysis showed that the marker remained a risk factor for death, which showed trend variation (P for trend <0.001). Subgroup forest plot analysis showed robustness in the predictive ability of NLR after exclusion of confounders. Besides, we demonstrated through Kaplan-Meier (KM) survival analysis curve that high risk NLR mortality substantially exceeded low risk NLR. The combined prediction of NLR and APACHEII achieved higher efficacy than NLR and APACHEII alone (AUC = 0.880, 95% CI [0.8280, 0.9290]). Additionally, Delong test indicated that the combined prediction demonstrated a significantly greater ROC than NLR and APACHEII alone, while DCA showed a considerably higher clinical net benefit rate. Increased NLR is a high risk factor and has predictive value for death in individuals with severe heatstroke. Suggestively, combination of NLR and APACHEII have greater predictive value.
Keywords: APACHEII; Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; Prognosis; Severe heatstroke.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lactate combined with SOFA score for improving the predictive efficacy of SOFA score in patients with severe heatstroke.Am J Emerg Med. 2024 Apr;78:163-169. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2024.01.033. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Am J Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 38295465
-
[Comparison of simplified acute physiology score III and other scoring systems in prediction of 28-day prognosis in patients with severe sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015 Jun;27(6):454-9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2015.06.008. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 26049183 Chinese.
-
[Predictive value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio on 28-day mortality of patients with severe pneumonia].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Jul;31(7):827-831. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.07.006. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 31441404 Chinese.
-
[The value of combination of the mortality in emergency department sepsis score and blood lactate level in the risk stratification of severe sepsis in the emergency department].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014 Mar;26(3):159-64. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2014.03.007. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014. PMID: 24598288 Chinese.
-
A NOMOGRAM FOR PREDICTING PATIENTS WITH SEVERE HEATSTROKE.Shock. 2022 Aug 1;58(2):95-102. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001962. Epub 2022 Jul 24. Shock. 2022. PMID: 35953457
Cited by
-
Effects of ulinastatin on therapeutic outcomes and inflammatory markers in pediatric septic shock patients.Sci Rep. 2025 May 13;15(1):16624. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00629-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40360546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kondo Y., Hifumi T., Shimazaki J., Oda Y., Shiraishi S.I., Hayashida K., et al. Comparison between the Bouchama and Japanese association for acute medicine heatstroke criteria with regard to the diagnosis and prediction of mortality of heatstroke patients: a multicenter observational study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health. 2019;16 doi: 10.3390/ijerph16183433. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

