Pulmonary actinomycosis mimicking lung malignancy: About two cases
- PMID: 37767510
- PMCID: PMC10520318
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20070
Pulmonary actinomycosis mimicking lung malignancy: About two cases
Abstract
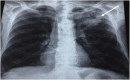
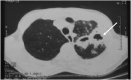
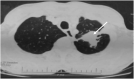
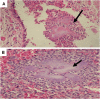
Pulmonary actinomycosis is a rare anaerobic infection with non specific clinical and radiographic presentations that delay diagnosis. Throughout literature, a significant number of misdiagnosed cases have been reported. The diagnosis is substantially based on histopathological pattern. We describe the cases of two patients evaluated and treated in pulmonary department 1 of Abderrahmane Mami hospital of Tunisia with a diagnosis of pulmonary actinomycosis. There are two men. The first patient had hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and the second one underwent surgery for bronchiectasis. Clinical presentation was consistent with productive cough, hemoptysis, and deterioration of general status. The medical examination was non-specific. The chest X-ray revealed an apical opacity, excavated in the first case and retractable in the second one. Biology showed an inflammatory syndrome. Bronchoscopy was performed in the two cases and showed lesions mimicking lung malignancy. Diagnosis is confirmed by histopathological examinations of surgical specimens in the two cases. Both patients were received antibiotic therapy. The results were excellent with a favorable clinical course and no deaths. This study highlights the misleading patterns of actinomycosis to prompt accurate diagnosis and earlier treatment, thus improving the outcome. Given either its low culture yield or the limited use of new molecular diagnostic tools in routine clinical practice, histological examination of lung tissue specimens is crucial to get the correct diagnosis.
Keywords: Antibiotics; Histological examination; Lung cancer; Pulmonary actinomycosis.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Wong V.K., Turmezei T., Weston V. Actinomycosis. Bmj. 2011:343. - PubMed
-
- Weissferdt A. Springer International Publishing; Cham: 2020. Infectious Lung Disease. Diagnostic Thoracic Pathology; pp. 3–71.
-
- Vidaur Na A.O., Vidaur E.A., et al. Solitary pulmonary nodule, pulmonary actinomycosis of chronic, report. Eac. Solitary pulmonary nodule, pulmonary actinomycosis of chronic evolution: a case report. Electronic J Biol. 2017;13(3) 265-8.
-
- Skuhala T., Vukelić D., Desnica B., Balen-Topić M., Stanimirović A., Višković K. Unusual presentations of actinomycosis: a case series and literature review. The Journal of Infection in Developing Countries. 2021;15(6):892–896. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

