Tracing the evolving dynamics and research hotspots of microbiota and immune microenvironment from the past to the new era
- PMID: 37768071
- PMCID: PMC10581186
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.00135-23
Tracing the evolving dynamics and research hotspots of microbiota and immune microenvironment from the past to the new era
Abstract
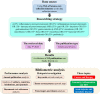
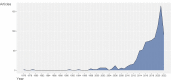
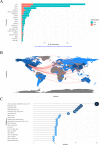
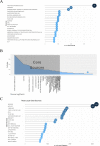
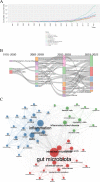
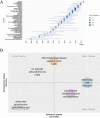
Gut microbiota can regulate many physiological processes within gastrointestinal tract and other distal sites. Dysbiosis may not only influence chronic diseases like the inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), metabolic disease, tumor and its therapeutic efficacy, but also deteriorate acute injuries. This article aims to review the documents in this field and summarize the research hotspots as well as developing processes. Gut microbiota and immune microenvironment-related documents from 1976 to 2022 were obtained from the Web of Science Core Collection database. Bibliometrics was used to assess the core authors and journals, most contributive countries and affiliations together with hotspots in this field and keyword co-occurrence analysis. Data were visualized to help comprehension. Nine hundred and twelve documents about gut microbiota and immune microenvironment were retrieved, and the annual publications increased gradually. The most productive author, country, and affiliation were "Zitvogel L," USA and "UNIV TEXAS MD ANDERSON CANC CTR," respectively. FRONTIERS IN IMMUNOLOGY, CANCERS, and INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SCIENCE were the periodicals with most publications. Keyword co-occurrence analysis identified three clusters, including gut microbiota, inflammation, and IBD. Combined with the visualized analysis of documents and keyword co-occurrence as well as literature reading, we recognized three key topics of gut microbiota: cancer and therapy; immunity, inflammation and IBD; acute injuries and metabolic diseases. This article revealed researches on gut microbiota and immune microenvironment were growing. More attention should be given to the latest hotspots like gut microbiota, inflammation, IBD, cancer and immunotherapy, acute traumas, and metabolic diseases.IMPORTANCEGut microbiota can regulate many physiological processes within gastrointestinal tract and other distal sites. Dysbiosis may not only influence chronic diseases like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), metabolic disease, tumor and its therapeutic efficacy, but also deteriorate acute injuries. While the application of bibliometrics in the field of gut microbiota and immune microenvironment still remains blank, which focused more on the regulation of the gut microbiota on the immune microenvironment of different kinds of diseases. Here, we intended to review and summarize the presented documents in gut microbiota and immune microenvironment field by bibliometrics. And we revealed researches on gut microbiota and immune microenvironment were growing. More attention should be given to the latest hotspots like gut microbiota, inflammation, IBD, cancer and immunotherapy, acute traumas, and metabolic diseases.
Keywords: acute injury; bibliometric analysis; cancer; gut microbiota; immune microenvironment; immunotherapy; inflammation; metabolic diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

