Purposeful and purposeless aging: Structural issues for sense of purpose and their implications for predicting life outcomes
- PMID: 37768600
- PMCID: PMC10840820
- DOI: 10.1037/dev0001633
Purposeful and purposeless aging: Structural issues for sense of purpose and their implications for predicting life outcomes
Abstract
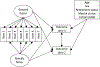
Despite the value of sense of purpose during older adulthood, this construct often declines with age. With some older adults reconsidering the relevance of purpose later in life, the measurement of purpose may suffer from variance issues with age. The current study investigated whether sense of purpose functions similarly across ages and evaluated if the predictive power of purpose on mental, physical, cognitive, and financial outcomes changes when accounting for a less age-affected measurement structure. Utilizing data from two nationwide panel studies (Health and Retirement Study: n = 14,481; Midlife in the United States: n = 4,030), the current study conducted local structural equation modeling and found two factors for the positively and negatively valenced purpose items in the Purpose in Life subscale (Ryff, 1989), deemed the purposeful and purposeless factor. These factors become less associated with each other at higher ages. When reproducing past findings with this two-factor structure, the current study found that the purposeful and purposeless factors predicted these outcomes in the same direction as would be suggested by past research, but the magnitude of these effects differed for some outcomes. The discussion focuses on the implications of what this means for our understanding of sense of purpose across the lifespan. (PsycInfo Database Record (c) 2024 APA, all rights reserved).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests to report. We used freely available panel data for this study, which can be accessed via (MIDUS:
Figures






References
-
- Ausmees L, Kandler C, Realo A, Allik J, Borkenau P, Hřebíčková M, & Mõttus R (2022). Age differences in personality traits and social desirability: A multi-rater multi-sample study. Journal of Research in Personality, 99, 104245.
-
- Batchelor JH, & Miao C (2016). Extreme response style: A meta-analysis. Journal of Organizational Psychology, 16(2), 51.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

