Adopting duplex sequencing technology for genetic toxicity testing: A proof-of-concept mutagenesis experiment with N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU)-exposed rats
- PMID: 37770135
- PMCID: PMC10539650
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2023.503669
Adopting duplex sequencing technology for genetic toxicity testing: A proof-of-concept mutagenesis experiment with N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU)-exposed rats
Abstract
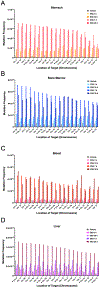
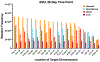
Duplex sequencing (DS) is an error-corrected next-generation sequencing method in which molecular barcodes informatically link PCR-copies back to their source DNA strands, enabling computational removal of errors in consensus sequences. The resulting background of less than one artifactual mutation per 107 nucleotides allows for direct detection of somatic mutations. TwinStrand Biosciences, Inc. has developed a DS-based mutagenesis assay to sample the rat genome, which can be applied to genetic toxicity testing. To evaluate this assay for early detection of mutagenesis, a time-course study was conducted using male Hsd:Sprague Dawley SD rats (3 per group) administered a single dose of 40 mg/kg N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU) via gavage, with mutation frequency (MF) and spectrum analyzed in stomach, bone marrow, blood, and liver tissues at 3 h, 24 h, 7 d, and 28 d post-exposure. Significant increases in MF were observed in ENU-exposed rats as early as 24 h for stomach (site of contact) and bone marrow (a highly proliferative tissue) and at 7 d for liver and blood. The canonical, mutational signature of ENU was established by 7 d post-exposure in all four tissues. Interlaboratory analysis of a subset of samples from different tissues and time points demonstrated remarkable reproducibility for both MF and spectrum. These results demonstrate that MF and spectrum can be evaluated successfully by directly sequencing targeted regions of DNA obtained from various tissues, a considerable advancement compared to currently used in vivo gene mutation assays.
Keywords: DuplexSeq™; EcNGS; Error-corrected NGS; Pig-a gene mutation assay; Rat-50 mutagenesis assay; Transgenic rodent assay.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest G.A.P., F.Y.L, J.E.H., E.K.S., L.N.W., D.N., C.C.V., and J.J.S. are employees (or former employees) and equity holders of TwinStrand Biosciences, Inc. F.Y.L, E.K.S., L.N.W., C.C.V., and J.J.S. are authors on one or more duplex sequencing-related patents.
Figures

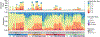
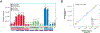
Update of
-
Adopting Duplex Sequencing™ Technology for Genetic Toxicity Testing: A Proof-of-Concept Mutagenesis Experiment with N-Ethyl-N-Nitrosourea (ENU)-Exposed Rats.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 9:2023.05.08.539833. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.08.539833. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2023 Oct;891:503669. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2023.503669. PMID: 37214853 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- OECD, Test No. 471: Bacterial Reverse Mutation Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4; 10.1787/9789264071247-en, 2020. (accessed 6 April 2023). - DOI
-
- OECD, Test No. 476: In Vitro Mammalian Cell Gene Mutation Tests using the Hprt and xprt genes, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4; 10.1787/9789264264809-en, 2016. (accessed 6 April 2023). - DOI
-
- OECD, Test No. 490: In Vitro Mammalian Cell Gene Mutation Tests Using the Thymidine Kinase Gene, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4; 10.1787/9789264264908-en, 2016. (accessed 6 April 2023). - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

