Deriving Novel Quaternary Ammonium Compound Disinfectant Scaffolds from a Natural Product: Mechanistic Insights of the Quaternization of Ianthelliformisamine C
- PMID: 37770411
- PMCID: PMC10841702
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.202300253
Deriving Novel Quaternary Ammonium Compound Disinfectant Scaffolds from a Natural Product: Mechanistic Insights of the Quaternization of Ianthelliformisamine C
Abstract
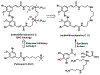
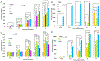
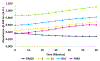
In the search for novel quaternary ammonium compound (QAC) disinfectants that can evade bacterial resistance, we turned to natural products as a source of inspiration. Herein we used natural product ianthelliformisamine C as a scaffold to design a small library of QACs. We first synthesized ianthelliformisamine C via an amide coupling that allowed for facile purification without the need for protecting groups. We then alkylated and quaternized the internal amines to yield four novel QACs, but all but one demonstrated no antibacterial activity against the tested strains. Using a combination of membrane depolarization and permeabilization assays, we were able to demonstrate that ianthelliformisamine C and the active QAC analog enact cell death via membrane permeabilization, contrary to prior reports on ianthelliformisamine C's mechanism of action.
Keywords: P. aeruginosa; antibiotics; mechanism of action; natural products; quaternary ammonium compounds.
© 2023 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Figures
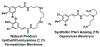
References
-
- Buffet-Bataillon S, Tattevin P, Bonnaure-Mallet M, Jolivet-Gougeon A, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 39, 381–389. - PubMed
-
- Denyer SP, Int. Biodeterior. 1990, 26, 89–100.
-
- Denyer SP, Stewart GSAB, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 1998, 41, 261–268.
-
- Lambert PA, Hammond SM, BBRC 1973, 54, 796–799. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

