Liquid-liquid phase separation within fibrillar networks
- PMID: 37770446
- PMCID: PMC10539382
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41528-8
Liquid-liquid phase separation within fibrillar networks
Abstract
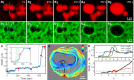
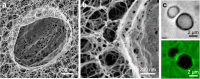
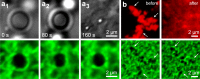
Complex fibrillar networks mediate liquid-liquid phase separation of biomolecular condensates within the cell. Mechanical interactions between these condensates and the surrounding networks are increasingly implicated in the physiology of the condensates and yet, the physical principles underlying phase separation within intracellular media remain poorly understood. Here, we elucidate the dynamics and mechanics of liquid-liquid phase separation within fibrillar networks by condensing oil droplets within biopolymer gels. We find that condensates constrained within the network pore space grow in abrupt temporal bursts. The subsequent restructuring of condensates and concomitant network deformation is contingent on the fracture of network fibrils, which is determined by a competition between condensate capillarity and network strength. As a synthetic analog to intracellular phase separation, these results further our understanding of the mechanical interactions between biomolecular condensates and fibrillar networks in the cell.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Nishi T, Wang TT, Kwei TK. Thermally induced phase separation behavior of compatible polymer mixtures. Macromolecules. 1975;8:227–234. doi: 10.1021/ma60044a025. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

