Long-term outcome and eligibility of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma over 3.0 cm in diameter
- PMID: 37770523
- PMCID: PMC10539460
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-43516-w
Long-term outcome and eligibility of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma over 3.0 cm in diameter
Abstract
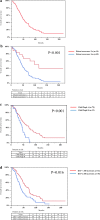
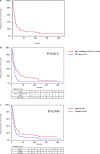
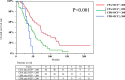
Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is effective for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with a diameter ≤ 3.0 cm. The present study aimed to elucidate the prognostic factors and clarify the indication of treatment for RFA outcomes in patients with HCC with a diameter > 3.0 cm. Among 2188 patients with HCC who underwent RFA, 100 patients with HCC with a diameter > 3.0 cm were enrolled in this study between August, 2000 and August, 2021. We analyzed local therapeutic efficacy, long-term outcomes, and prognostic factors in patients with HCC with a diameter > 3.0 cm. Among all patients, 77 patients achieved complete ablation in one session. There were no treatment-related deaths or major complications. Local tumor recurrence occurred in 48% (n = 48) of the patients, and distant tumor recurrence occurred in 82% (n = 82) of the patients during the study period. The survival rates at 1-, 3-, 5-, 10-, and 15- years were 93.0%, 66.0%, 40.0%, 15.5%, and 10.2%, respectively. Cox proportional hazards regression analysis confirmed that distant tumor recurrence, Child-Pugh class B, and pre-ablation des-γ-carboxy prothrombin (DCP) levels ≥ 200 mAU/mL were independent unfavorable prognostic factors with a hazard ratio of 3.34 (95% CI, 1.57-7.11; P = 0.002), 2.43 (95% CI, 1.35-4.37; P = 0.003), and 1.83 (95% CI, 1.14-2.93; P = 0.012), respectively. In conclusion, patients with HCC with a diameter > 3.0 cm with Child-Pugh class A and DCP levels < 200 mAU/mL might be eligible for RFA treatment.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

