Thyroid autoimmunity and future pregnancy outcome in women of recurrent pregnancy loss: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 37770816
- PMCID: PMC10643810
- DOI: 10.1007/s10815-023-02933-6
Thyroid autoimmunity and future pregnancy outcome in women of recurrent pregnancy loss: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Thyroid autoimmunity (TAI) has been associated with the risk of recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL). This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted to evaluate the influence of TAI on subsequent pregnancy outcome of women with RPL.
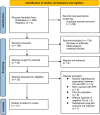
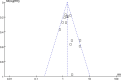
Methods: A systematic search of Medline, Web of Science, and Embase was conducted to identify studies evaluating the influence of TAI on subsequent risk of pregnancy loss (PL) in women with RPL. Study quality was evaluated via the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. A random-effects model was utilized to pool the results, accounting for heterogeneity.
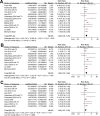
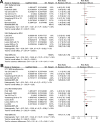
Results: Ten observational studies were included. Compared to women without thyroid autoantibodies, RPL women with TAI had a higher risk of PL in their subsequent pregnancy (risk ratio [RR]: 1.46. 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.20 to 1.78, p < 0.001; I2 = 35%). Sensitivity analyses showed consistent results in studies with thyroid peroxidase antibody positivity (RR: 1.50, 95% CI: 1.23 to 1.82) and in studies with TAI assessed before pregnancy (RR: 1.28, 95% CI: 1.07 to 1.53). Subgroup analyses showed that the results were not significantly different in prospective and retrospective studies, in RPL defined as at least two or three PL, in euthyroid women and women with euthyroidism or subclinical hypothyroidism, in women with and without levothyroxine treatment, in studies reporting first-trimester or overall PL, and in studies with different quality scores (p for subgroup difference all > 0.05).
Conclusions: In women with RPL, positive for TAI may be related to a higher risk of PL in subsequent pregnancy.
Keywords: Levothyroxine; Meta-analysis; Recurrent pregnancy loss; Thyroid autoimmunity; Thyroid peroxidase antibody.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of levothyroxine supplementation on pregnancy loss and preterm birth in women with subclinical hypothyroidism and thyroid autoimmunity: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Hum Reprod Update. 2019 May 1;25(3):344-361. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz003. Hum Reprod Update. 2019. PMID: 30951172
-
Subclinical hypothyroidism and thyroid autoimmunity in recurrent pregnancy loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Fertil Steril. 2020 Mar;113(3):587-600.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2019.11.003. Fertil Steril. 2020. PMID: 32192591
-
Prevalence of thyroid autoimmunity and effect of levothyroxine treatment in a cohort of 1064 patients with recurrent pregnancy loss.Reprod Biomed Online. 2020 Apr;40(4):582-592. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2019.11.014. Epub 2019 Nov 30. Reprod Biomed Online. 2020. PMID: 32160949
-
Prevalence of Thyroid Autoimmunity in Women with Recurrent Pregnancy Loss.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Jan 22;57(2):96. doi: 10.3390/medicina57020096. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 33499017 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid autoimmunity and IVF/ICSI outcomes in euthyroid women: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2020 Nov 25;18(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12958-020-00671-3. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 33239046 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Risk prediction for recurrent pregnancy loss based on routine inspections in the first trimester of pregnancy, a retrospective study in China.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 9;12:1476722. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1476722. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40270497 Free PMC article.
-
Association between antinuclear antibodies status and preterm birth in Japanese pregnant women: a prospective cohort study from Adjunct Study of the Japan Environment and Children's Study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Dec 28;24(1):879. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-07084-9. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 39732712 Free PMC article.
-
The association of thyroid autoimmunity with ovarian reserve in women with type 1 diabetes with and without polycystic ovary syndrome.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 8;14(1):13223. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63741-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38851814 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

