Association between a high triglyceride-glucose index and chronic kidney disease in adult patients with latent autoimmune diabetes
- PMID: 37770895
- PMCID: PMC10540360
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-023-01465-5
Association between a high triglyceride-glucose index and chronic kidney disease in adult patients with latent autoimmune diabetes
Abstract
Background: Insulin resistance (IR) is one of the risk factors for chronic kidney disease (CKD) and diabetes. The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index is considered a reliable alternative marker of IR. We investigated the correlation between the TyG index and the severity of CKD in patients with latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA).
Methods: This cross-sectional study included 288 patients with LADA in the department of endocrinology at our hospital between January 2018 and January 2022. The TyG index was calculated as Ln [TG (mg/dl) × fasting blood glucose (FBG) (mg/dl) / 2]. All individuals were divided into either a LADA + CKD group or a LADA + non-CKD group according to the presence or absence of CKD. A correlation analysis, logistic regression analysis and receiver operating characteristics curve analysis were performed.
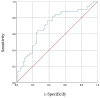
Results: A total of 130 (45.1%) participants were identified as having CKD. Compared with the non-CKD group, the CKD group had a longer disease duration and a higher proportion of smokers; patients were more likely to have hypertension and higher serum creatinine, triglyceride, cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, FBG, uric acid estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFR) and TyG levels as well as lower high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels (all P < 0.05). The positive relationship between the TyG index and the urinary albumin/creatinine ratio was significant (r = 0.249, P = 0.010). There was also a significant correlation between the TyG index and the eGFR (r = - 0.211, P = 0.034) after adjusting for confounding factors. The area-under-the-curve value of the TyG index was 0.708 (95% confidence interval: 0.61-0.81, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: The TyG index is significantly associated with the severity of CKD in patients with LADA. This conclusion supports the clinical application of the TyG index for the assessment of kidney disease in patients with LADA.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Insulin resistance; Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults; Triglyceride–glucose index.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Classification of diabetes mellitus. Geneva, World Health Organization.; 2019.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous