RU.521 mitigates subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced brain injury via regulating microglial polarization and neuroinflammation mediated by the cGAS/STING/NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 37770901
- PMCID: PMC10537158
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-023-01274-2
RU.521 mitigates subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced brain injury via regulating microglial polarization and neuroinflammation mediated by the cGAS/STING/NF-κB pathway
Erratum in
-
Correction: RU.521 mitigates subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced brain injury via regulating microglial polarization and neuroinflammation mediated by the cGAS/STING/NF-κB pathway.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Aug 6;22(1):390. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01772-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39107840 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The poor prognosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is often attributed to neuroinflammation. The cGAS-STING axis, a cytoplasmic pathway responsible for detecting dsDNA, plays a significant role in mediating neuroinflammation in neurological diseases. However, the effects of inhibiting cGAS with the selective small molecule inhibitor RU.521 on brain injury and the underlying mechanisms after SAH are still unclear.
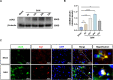
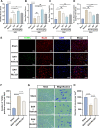
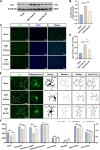
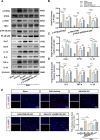
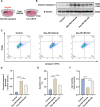
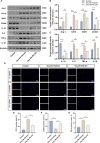
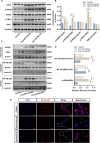
Methods: The expression and microglial localization of cGAS following SAH were investigated with western blot analysis and immunofluorescent double-staining, respectively. RU.521 was administered after SAH. 2'3'-cGAMP, a second messenger converted by activated cGAS, was used to activate cGAS-STING. The assessments were carried out by adopting various techniques including neurological function scores, brain water content, blood-brain barrier permeability, western blot analysis, TUNEL staining, Nissl staining, immunofluorescence, morphological analysis, Morris water maze test, Golgi staining, CCK8, flow cytometry in the in vivo and in vitro settings.
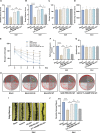
Results: Following SAH, there was an observed increase in the expression levels of cGAS in rat brain tissue, with peak levels observed at 24 h post-SAH. RU.521 resulted in a reduction of brain water content and blood-brain barrier permeability, leading to an improvement in neurological deficits after SAH. RU.521 had beneficial effects on neuronal apoptosis and microglia activation, as well as improvements in microglial morphology. Additionally, RU.521 prompted a shift in microglial phenotype from M1 to M2. We also noted a decrease in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, and an increase in the level of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. Finally, RU.521 treatment was associated with improvements in cognitive function and an increase in the number of dendritic spines in the hippocampus. The therapeutic effects were mediated by the cGAS/STING/NF-κB pathway and were found to be abolished by 2'3'-cGAMP. In vitro, RU.521 significantly reduced apoptosis and neuroinflammation.
Conclusion: The study showed that SAH leads to neuroinflammation caused by microglial activation, which contributes to early brain injury. RU.521 improved neurological outcomes and reduced neuroinflammation by regulating microglial polarization through the cGAS/STING/NF-κB pathway in early brain injury after SAH. RU.521 may be a promising candidate for the treatment of neuroinflammatory pathology after SAH. Video Abstract.
Keywords: Early brain injury; Microglia; NF-κB; Neuroinflammation; STING; Subarachnoid hemorrhage; cGAS.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang T, Wu P, Budbazar E, Zhu Q, Sun C, Mo J, Peng J, Gospodarev V, Tang J, Shi H, Zhang JH. Mitophagy Reduces Oxidative Stress Via Keap1 (Kelch-Like Epichlorohydrin-Associated Protein 1)/Nrf2 (Nuclear Factor-E2-Related Factor 2)/PHB2 (Prohibitin 2) Pathway After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats. Stroke. 2019;50:978–88. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.021590 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tian Y, Liu B, Li Y, Zhang Y, Shao J, Wu P, Xu C, Chen G, Shi H. Activation of RARalpha Receptor Attenuates Neuroinflammation After SAH via Promoting M1-to-M2 Phenotypic Polarization of Microglia and Regulating Mafb/Msr1/PI3K-Akt/NF-kappaB Pathway. Front Immunol. 2022;13:839796. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.839796 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021Y10/Young Medical Talent Funding Project of The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University
- YQ2019H05/Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China
- 82071309/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022ZX06C03/Key Research and Development Plan Project of Heilongjiang Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

