Effect of low-pressure pneumoperitoneum on pain and inflammation in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 37770908
- PMCID: PMC10540329
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-023-06492-y
Effect of low-pressure pneumoperitoneum on pain and inflammation in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Objective: We aim to assess the effect of low-pressure pneumoperitoneum on post operative pain and ten of the known inflammatory markers.
Background: The standard of care pneumoperitoneum set pressure in laparoscopic cholecystectomy is set to 12-14 mmHg, but many societies advocate to operate at the lowest pressure allowing adequate exposure of the operative field. Many trials have described the benefits of operating at a low-pressure pneumoperitoneum in terms of lower post operative pain, and better hemodynamic stability. But only few describe the effects on inflammatory markers and cytokines.
Methods: A prospective, double-blinded, randomised, controlled clinical trial, including patients who underwent elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Patients randomised into low-pressure (8-10 mmHg) vs. standard-pressure (12-14 mmHg) with an allocation ratio of 1:1. Perioperative variables were collected and analysed.
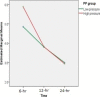
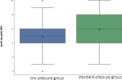
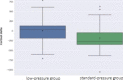
Results: one hundred patients were allocated, 50 patients in each study arm. Low-pressure patients reported lower median pain score 6-hour post operatively (5 vs. 6, p-value = 0.021) in comparison with standard-pressure group. Eight out of 10 inflammatory markers demonstrated better results in low-pressure group in comparison with standard-pressure, but the effect was not statistically significant. Total operative time and surgery difficulty was not significantly different between the two groups even in the hands of inexperienced surgeons.
Conclusion: low-pressure laparoscopic cholecystectomy is associated with less post operative pain and lower rise of inflammatory markers. It is feasible with comparable complications to the standard of care. Registered on ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT05530564/ September 7th, 2022).
Keywords: Clinical trial; Inflammatory marker; Laparoscopic cholecystectomy; Low pressure insufflation; Pain; Pneumoperitoneum.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of inflammatory markers in low-pressure pneumoperitoneum with deep neuromuscular block versus standard pressure pneumoperitoneum among patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy for gallstone disease: a randomized control trial.Surg Endosc. 2024 Aug;38(8):4648-4656. doi: 10.1007/s00464-024-11026-z. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Surg Endosc. 2024. PMID: 38977504 Clinical Trial.
-
Low-pressure pneumoperitoneum versus standard pneumoperitoneum in laparoscopic cholecystectomy, a prospective randomized clinical trial.Surg Endosc. 2009 May;23(5):1044-7. doi: 10.1007/s00464-008-0119-2. Epub 2008 Sep 23. Surg Endosc. 2009. PMID: 18810547 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative study of low pressure versus standard pressure pneumoperitoneum in laparoscopic cholecystectomy--a randomised controlled trial.Trop Gastroenterol. 2009 Jul-Sep;30(3):171-4. Trop Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 20306755 Clinical Trial.
-
The Impact of Intraoperative CO 2 Pneumoperitoneum Pressure in Gastrointestinal Surgery: A Systematic Review.Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2025 Apr 1;35(2):e1325. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000001325. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2025. PMID: 39925242 Free PMC article.
-
Low-pressure versus standard-pressure pneumoperitoneum in minimally invasive colorectal surgery: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression analysis.Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2024 Jul 19;12:goae052. doi: 10.1093/gastro/goae052. eCollection 2024. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2024. PMID: 39036068 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of inflammatory markers in low-pressure pneumoperitoneum with deep neuromuscular block versus standard pressure pneumoperitoneum among patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy for gallstone disease: a randomized control trial.Surg Endosc. 2024 Aug;38(8):4648-4656. doi: 10.1007/s00464-024-11026-z. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Surg Endosc. 2024. PMID: 38977504 Clinical Trial.
-
Low-Pressure Versus Normal-Pressure Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy and its Effect on Intra-Operative Parameters and Post-Operative Pain: An Observational Study.Niger Med J. 2025 Jun 16;66(2):715-723. doi: 10.71480/nmj.v66i2.768. eCollection 2025 Mar-Apr. Niger Med J. 2025. PMID: 40703904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gohil A. Comparison of low pressure versus standard pressure pneumoperitoneum for elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy in a tertiary care institute of western India. Int Surg J. 2018;5(5):1776. doi: 10.18203/2349-2902.isj20181569. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

