Anlotinib combined with whole-brain radiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer with multiple brain metastases that progressed or developed after at least one lines of prior treatment
- PMID: 37771446
- PMCID: PMC10523148
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1169333
Anlotinib combined with whole-brain radiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer with multiple brain metastases that progressed or developed after at least one lines of prior treatment
Abstract
Background: Intracranial metastasis that failed standard systematic treatment is common in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), contributing significantly to morbidity and mortality. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of anlotinib combined with whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) for NSCLC with brain metastases (BMs) that progressed or developed after at least one line of prior treatment and compare the outcomes with that of the contemporary institutional control.
Methods: NSCLC patients with multiple BMs that progressed or developed after at least one line of prior systematic treatment and treated with WBRT subsequently between 2019 and 2021 were selected retrospectively for analysis. Based on whether concurrent anlotinib had been used in combination with WBRT, the cases were divided into the anlotinib group and control group. The primary endpoints were intracranial progression-free survival (iPFS) and safety.
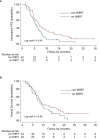
Results: A total of 76 patients met the inclusion criteria of the study. Of the 76 patients, 34 received concurrent WBRT and anlotinib followed by anlotinib maintenance and 42 were treated with WBRT alone or in combination with other systemic agents at the physicians' discretion. The median follow-up for the entire cohort was 21 months. The median iPFS for the anlotinib and control group was 6.7 months (95% CI, 4.6-9.9) and 5.3 months (95% CI, 4.0-6.5), respectively (log-rank P = 0.04). There was no difference in overall survival between the two groups (log-rank P = 0.38). In the anlotinib group, treatment-related adverse events were reported in 15 patients (44.1%), with acute or late grade 3-5 adverse events identified in 14.7% of patients (n = 5).
Conclusions: WBRT plus anlotinib, as a convenient chemo-free regimen, may represent an overall safe and effective procedure in advanced NSCLC with multiple BMs that progressed or developed after standard systematic treatment.
Keywords: antiangiogenic TKIs; brain metastases; later-line; non-small cell lung cancer; whole-brain radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2023 Kong, Yu, Qian, Song, Wen, Jiang, Zhu, Xu, Zhao, Guo, Wu, He and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mulvenna P, Nankivell M, Barton R, Faivre-Finn C, Wilson P, McColl E, et al. . Dexamethasone and supportive care with or without whole brain radiotherapy in treating patients with non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases unsuitable for resection or stereotactic radiotherapy (QUARTZ): results from a phase 3, non-inferiority, randomised trial. Lancet (2016) 388(10055):2004–14. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30825-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous