E-cadherin Expression in Premalignant Lesions, Premalignant Conditions, Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and Normal Mucosa: An Immunohistochemical Study
- PMID: 37772225
- PMCID: PMC10528546
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.44266
E-cadherin Expression in Premalignant Lesions, Premalignant Conditions, Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and Normal Mucosa: An Immunohistochemical Study
Abstract
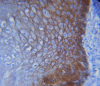
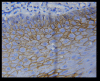
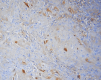
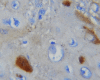
Background Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is a multi-step process. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is an important step in the progression of OSCC. One of the components that influence EMT is E-cadherin. The aim of this study was to determine the expression of E-cadherin in oral submucous fibrosis (OSMF), various grades of epithelial dysplasia, OSCC, and to compare it with the expression in the normal mucosa. Material and methods E-cadherin immunohistochemical detection was done using a monoclonal antibody of clone EP-6TM and the PolyExcel HRP/DAB chromogen detection system. A total of 100 samples, were divided into four groups, which included epithelial dysplasia (group 2) (30 cases), oral submucous fibrosis (group 3) (OSMF-30 cases), and oral squamous cell carcinoma (group 4) (OSCC-30 cases), which was compared with normal mucosa (group 1) (10 cases). The positive control used for E-cadherin was ductal breast carcinoma. Results All the cases of normal mucosa, epithelial dysplasia, and OSMF showed positivity for E-cadherin expression. In OSCC, 97% of cases expressed E-cadherin except one case. Out of 30 cases of epithelial dysplasia, 53% of mild epithelial dysplasia had a moderate intensity of expression and 75% had a mild intensity of E-cadherin expression. In moderately differentiated OSCC, 82% of cases showed mild intensity. Tissue localization of the E-cadherin stain in the basal layer decreased from normal mucosa to grades of epithelial dysplasia and OSCC. The pattern of E-cadherin staining in all the cases of group I, group II, and group III was membranous. In 97% of OSCC cases, both membranous and cytoplasmic staining were seen. Conclusion E-cadherin expression was reduced in increasing grades of epithelial dysplasia, OSCC, and OSMF compared to that of normal mucosa. E-cadherin expression is reduced as the lesions progress to malignancy. Hence, E-cadherin can be considered a surrogate marker of malignancy.
Keywords: e-cadherin; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; oral epithelial dysplasia; oral potentially malignant disorders; oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Copyright © 2023, Kalaimani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Molecular pathogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: implications for therapy. Choi S, Myers JN. J Dent Res. 2008;87:14–32. - PubMed
-
- Cadherin switching: essential for behavioral but not morphological changes during an epithelium-to-mesenchyme transition. Maeda M, Johnson KR, Wheelock MJ. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:873–887. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
